Administrative areas after the unification of the German Empire (1871–1918) |
|
| Native name | Deutsche Einigung |
|---|---|
| Date | 18 August 1866 – 18 January 1871 |
| Location | |
| Participants |
|
| Outcome |
|
The unification of Germany (German: Deutsche Einigung, pronounced [ˈdɔʏtʃə ˈʔaɪnɪɡʊŋ] (listen)) was the process of building the modern German nation-state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria of the Habsburgs), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of the North German Confederation Treaty establishing the North German Confederation, initially a Prussian-dominated military alliance which was subsequently deepened through adoption of the North German Constitution. The process symbolically concluded with the ceremonial proclamation of the German Empire i.e. the German Reich having 25 member states and led by the Kingdom of Prussia of the Hohenzollerns on 18 January 1871; the event was later celebrated as the customary date of the German Empire’s foundation, although the legally meaningful events relevant to the accomplishment of unification occurred on 1 January 1871 (accession of South German states and constitutional adoption of the name German Empire) and 4 May 1871 (entry into force of the permanent Constitution of the German Empire).
Despite the legal, administrative, and political disruption caused by the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the German-speaking people of the old Empire had a common linguistic, cultural, and legal tradition. European liberalism offered an intellectual basis for unification by challenging dynastic and absolutist models of social and political organization; its German manifestation emphasized the importance of tradition, education, and linguistic unity. Economically, the creation of the Prussian Zollverein (customs union) in 1818, and its subsequent expansion to include other states of the German Confederation, reduced competition between and within states. Emerging modes of transportation facilitated business and recreational travel, leading to contact and sometimes conflict between and among German-speakers from throughout Central Europe. The model of diplomatic spheres of influence resulting from the Congress of Vienna in 1814–15 after the Napoleonic Wars endorsed Austrian dominance in Central Europe through Habsburg leadership of the German Confederation, designed to replace the Holy Roman Empire. The negotiators at Vienna took no account of Prussia’s growing strength within and declined to create a second coalition of the German states under Prussia’s influence, and so failed to foresee that Prussia would rise to challenge Austria for leadership of the German peoples. This German dualism presented two solutions to the problem of unification: Kleindeutsche Lösung, the small Germany solution (Germany without Austria), or Großdeutsche Lösung, the greater Germany solution (Germany with Austria), ultimately settled in favor of the former solution in the Peace of Prague.
Historians debate whether Otto von Bismarck—Minister President of Prussia—had a master plan to expand the North German Confederation of 1866 to include the remaining independent German states into a single entity or simply to expand the power of the Kingdom of Prussia. They conclude that factors in addition to the strength of Bismarck’s Realpolitik led a collection of early modern polities to reorganize political, economic, military, and diplomatic relationships in the 19th century. Reaction to Danish and French nationalism provided foci for expressions of German unity. Military successes—especially those of Prussia—in three regional wars generated enthusiasm and pride that politicians could harness to promote unification. This experience echoed the memory of mutual accomplishment in the Napoleonic Wars, particularly in the War of Liberation of 1813–14. By establishing a Germany without Austria, the political and administrative unification in 1871 at least temporarily solved the problem of dualism.
Despite undergoing in the later years several further changes of its name and borders, overhauls of its constitutional system, periods of limited sovereignty and interrupted unity of its territory or government, and despite dissolution of its dominant founding federated state, the polity resulting from the unification process continues its existence, surviving until today in its contemporary form known as the Federal Republic of Germany.
Background[edit]
Early history[edit]
A confederated realm of German princedoms, along with some adjacent lands, had been in existence for over a thousand years; dating to the Treaty of Verdun i.e. the foundation of East Francia from eastern Frankish Empire (Francia) in 843, especially when the Ottonian dynasty took power to rule it in 919, though the Empire subsequently entered period of increasing fragmentation. These lands made up the territory of the Holy Roman Empire, which at times included more than 1,000 entities. The states ranged in size from the small and complex territories of the princely Hohenlohe family branches to sizable, well-defined territories such as the Electorate of Bavaria, the Margraviate of Brandenburg or the Kingdom of Bohemia. Their governance varied: they included free imperial cities, also of different sizes, such as the powerful Augsburg and the minuscule Weil der Stadt; ecclesiastical territories, also of varying sizes and influence, such as the wealthy Abbey of Reichenau and the powerful Archbishopric of Cologne; and dynastic states such as Württemberg. Among the German-speaking states, the Holy Roman Empire’s administrative and legal mechanisms provided a venue to resolve disputes between peasants and landlords, between jurisdictions, and within jurisdictions. Through the organization of imperial circles (Reichskreise), groups of states consolidated resources and promoted regional and organizational interests, including economic cooperation and military protection.
Early modern era and Eighteenth century[edit]
Since the 15th century, with few exceptions, the Empire’s Prince-electors had chosen successive heads of the House of Habsburg from the Duchy of Austria to hold the title of Holy Roman Emperor. Although they initially sought to restore central Imperial power, preserving a weak and fragmented Empire was convenient for France and Sweden, and therefore, their ensuing intervention led to the Peace of Westphalia which effectively thwarted for centuries any serious attempts to reinforce the imperial central authority and petrified fragmentation, resulting in the German-speaking territories comprising on the eve of the Napoleonic Wars still more than 300 political entities, most of them being parts of the Holy Roman Empire, though portions of the extensive Habsburg Monarchy (exclusively its large non-German-speaking territories: Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen and the Austrian partition of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth) or of the Hohenzollern Kingdom of Prussia (both the German-speaking former Duchy of Prussia and the non-German-speaking entire territory of the Prussian partition of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth) as well as the German-speaking Swiss cantons were outside of the Imperial borders. This became known as the practice of Kleinstaaterei, or «small-statery». As a further consequence, there was no German national identity in development as late as 1800, mainly due to the highly autonomous or semi-independent nature of the princely states; most inhabitants of the Holy Roman Empire, outside of those ruled by the emperor directly, identified themselves mainly with their prince rather than with the Empire or the nation as a whole. However, by the 19th century, transportation and communications improvements started to bring these regions closer together.[1]
Dissolution of the Old Empire by the Napoleonic Continental System[edit]
Invasion of the (mostly ceremonial at the time) HRR by the First French Empire in the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802) resulted in crushing the HRR and allied forces by Napoleon Bonaparte. The treaties of Lunéville (1801) and the Mediatization of 1803 secularized the ecclesiastical principalities and abolished most free imperial cities and these territories along with their inhabitants were absorbed by dynastic states. This transfer particularly enhanced the territories of Württemberg and Baden. In 1806, after a successful invasion of Prussia and the defeat of Prussia at the joint battles of Jena-Auerstedt 1806 during the War of the Third Coalition, Napoleon dictated the Treaty of Pressburg which included the formal dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire and the abdication of Emperor Francis II from the nominal reign over it. Napoleon established instead a German client state of France known as the Confederation of the Rhine which, inter alia, provided for the mediatization of over a hundred petty princes and counts and the absorption of their territories, as well as those of hundreds of imperial knights, by the Confederation’s member-states. Several states were promoted to kingdoms such as the Kingdom of Bavaria, the Kingdom of Saxony or the Kingdom of Hanover.[2] Following the formal secession from the Empire of the majority of its constituent states, the Emperor dissolved the Holy Roman Empire.[3]
Rise of German nationalism under Napoleon[edit]
Under the hegemony of the French Empire (1804–1814), popular German nationalism thrived in the reorganized German states. Due in part to the shared experience, albeit under French dominance, various justifications emerged to identify «Germany» as a potential future single state. For the German philosopher Johann Gottlieb Fichte,
The first, original, and truly natural boundaries of states are beyond doubt their internal boundaries. Those who speak the same language are joined to each other by a multitude of invisible bonds by nature herself, long before any human art begins; they understand each other and have the power of continuing to make themselves understood more and more clearly; they belong together and are by nature one and an inseparable whole.[4]
A common language may have been seen to serve as the basis of a nation, but as contemporary historians of 19th-century Germany noted, it took more than linguistic similarity to unify these several hundred polities.[5] The experience of German-speaking Central Europe during the years of French hegemony contributed to a sense of common cause to remove the French invaders and reassert control over their own lands. The Napoleon’s campaigns in Poland (1806–07) resulting in his decision to re-establish a form of Polish statehood (the Duchy of Warsaw) at the cost of also Prussian-conquered Polish territories, as well as his campaigns on Iberian Peninsula, in western Germany, and his disastrous invasion of Russia in 1812 disillusioned many Germans, princes and peasants alike. Napoleon’s Continental System nearly ruined the Central European economy. The invasion of Russia included nearly 125,000 troops from German lands, and the loss of that army encouraged many Germans, both high- and low-born, to envision a Central Europe free of Napoleon’s influence.[6] The creation of student militias such as the Lützow Free Corps exemplified this tendency.[7]
The debacle in Russia loosened the French grip on the German princes. In 1813, Napoleon mounted a campaign in the German states to bring them back into the French orbit; the subsequent War of Liberation culminated in the great Battle of Leipzig, also known as the Battle of Nations. In October 1813, more than 500,000 combatants engaged in ferocious fighting over three days, making it the largest European land battle of the 19th century. The engagement resulted in a decisive victory for the Coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Saxony, and Sweden. As a result, the Confederation of the Rhine collapsed and the French period came to an end. Success encouraged the Coalition forces to pursue Napoleon across the Rhine; his army and his government collapsed, and the victorious Coalition incarcerated Napoleon on Elba. During the brief Napoleonic restoration known as the 100 Days of 1815, forces of the Seventh Coalition, including an Anglo-Allied army under the command of the Duke of Wellington and a Prussian army under the command of Gebhard von Blücher, were victorious at Waterloo (18 June 1815).[8] The critical role played by Blücher’s troops, especially after having to retreat from the field at Ligny the day before, helped to turn the tide of combat against the French. The Prussian cavalry pursued the defeated French in the evening of 18 June, sealing the allied victory. From the German perspective, the actions of Blücher’s troops at Waterloo, and the combined efforts at Leipzig, offered a rallying point of pride and enthusiasm.[9] This interpretation became a key building block of the Borussian myth expounded by the pro-Prussian nationalist historians later in the 19th century.[10]
Congress of Vienna and the rise of German dualism[edit]
After Napoleon’s defeat, the Congress of Vienna established a new European political-diplomatic system based on the balance of power. This system reorganized Europe into spheres of influence, which, in some cases, suppressed the aspirations of the various nationalities, including the Germans and Italians.[11]
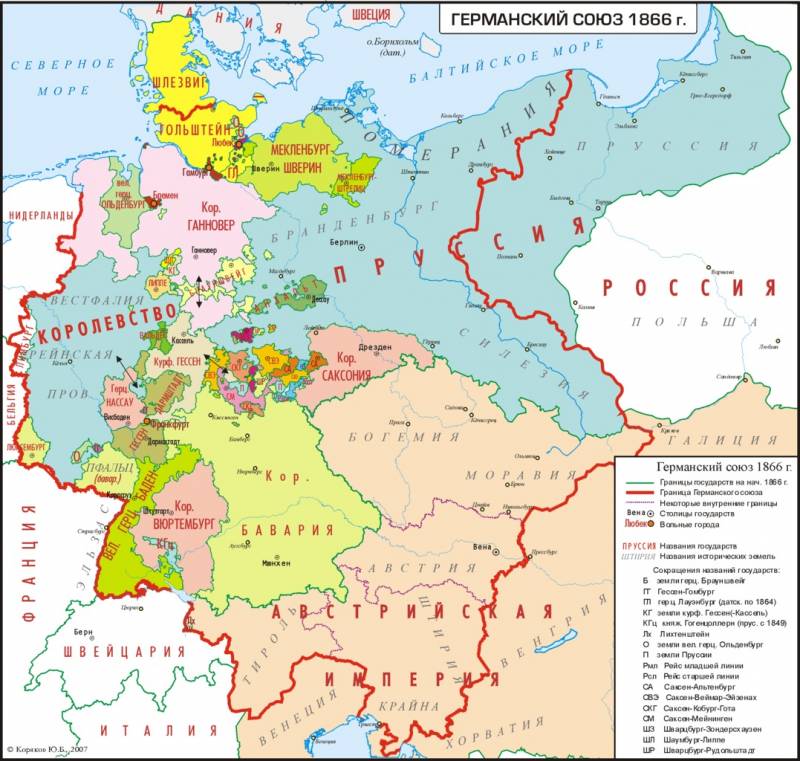
Generally, an enlarged Prussia and the 38 other states consolidated from the mediatized territories of 1803 were confederated within the Austrian Empire’s sphere of influence. The Congress established a loose German Confederation (1815–1866), headed by Austria, with a «Federal Diet» (called the Bundestag or Bundesversammlung, an assembly of appointed leaders) that met in the city of Frankfurt am Main. Its borders resembled those of its predecessor, the Holy Roman Empire (though there were some deviations e.g. Prussian territory in the Confederation was extended to include also the formerly Polish territories of the Lauenburg and Bütow Land and the former Starostwo of Draheim, while Austrian part was extended to include in the years 1818-1850 also the formerly Polish territories of the Duchy of Oświęcim and the Duchy of Zator), meaning that large portions of both Prussia and Austria were left outside pIn recognition of the imperial position traditionally held by the Habsburgs, the emperors of Austria became the titular presidents of this parliament. Despite the nomenclature of Diet (Assembly or Parliament), this institution should in no way be construed as a broadly, or popularly, elected group of representatives. Many of the states did not have constitutions, and those that did, such as the Duchy of Baden, based suffrage on strict property requirements which effectively limited suffrage to a small portion of the male population.[12]
Problems of reorganization[edit]
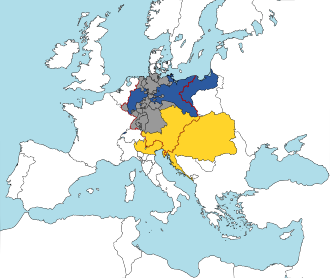
Boundaries of the German Confederation. Prussia is blue, Austria-Hungary yellow, and the rest grey.
Problematically, the built-in Austrian dominance failed to take into account Prussia’s 18th-century emergence in Imperial politics. This impractical solution did not reflect the new status of Prussia in the overall scheme. Although the Prussian army had been dramatically defeated in the 1806 Battle of Jena-Auerstedt, it had made a spectacular comeback at Waterloo. Consequently, Prussian leaders expected to play a pivotal role in German politics.[13] Ever since the Prince-Elector of Brandenburg had made himself King in Prussia at the beginning of that century, their domains had steadily increased through inheritance and war. Prussia’s consolidated strength had become especially apparent during the Partitions of Poland, the War of the Austrian Succession and the Seven Years’ War under Frederick the Great.[14] As Maria Theresa and Joseph tried to restore Habsburg hegemony in the Holy Roman Empire, Frederick countered with the creation of the Fürstenbund (Union of Princes) in 1785. Austrian-Prussian dualism lay firmly rooted in old Imperial politics. Those balance of power manoeuvers were epitomized by the War of the Bavarian Succession, or «Potato War» among common folk. Even after the end of the Holy Roman Empire, this competition influenced the growth and development of nationalist movements in the 19th century.[15]
Prelude[edit]
Vormärz[edit]
The period of Austrian and Prussian police-states and vast censorship between the Congress of Vienna and the Revolutions of 1848 in Germany later became widely known as the Vormärz, the «before March», referring to March 1848. During this period, European liberalism gained momentum; the agenda included economic, social, and political issues. Most European liberals in the Vormärz sought unification under nationalist principles, promoted the transition to capitalism, sought the expansion of male suffrage, among other issues. Their «radicalness» depended upon where they stood on the spectrum of male suffrage: the wider the definition of suffrage, the more radical.[16]
The surge of German nationalism, stimulated by the experience of Germans in the Napoleonic period and initially allied with liberalism, shifted political, social, and cultural relationships within the German states.[17] In this context, one can detect its roots in the experience of Germans in the Napoleonic period.[18] Furthermore, implicit and sometimes explicit promises made during the German Campaign of 1813 engendered an expectation of popular sovereignty and widespread participation in the political process, promises that largely went unfulfilled once peace had been achieved.[19]
Emergence of liberal nationalism and conservative response[edit]
In October, 1817, approximately 500 students rallied at Wartburg Castle, where Martin Luther had sought refuge over three centuries earlier, to demonstrate in favor of national unification. Wartburg was chosen for its symbolic connection to German national character. Contemporary colored wood engraving[20]
Pro-nationalist participants march to the ruins of Hambach Castle in 1832. Students and some professionals, and their spouses, predominated. They carried the flag of the underground Burschenschaft, which later became the basis of the flag of modern Germany.
A German caricature mocking the Carlsbad Decrees, which suppressed freedom of expression
Despite considerable conservative reaction, ideas of unity joined with notions of popular sovereignty in German-speaking lands. The Burschenschaft student organizations and popular demonstrations, such as those held at Wartburg Castle in October 1817, contributed to a growing sense of unity among German speakers of Central Europe.[21]
At the Wartburg Festival in 1817 the first real movements among the students were formed — fraternities and student organizations emerged. The colors black, red and gold were symbolic of this. Agitation by student organizations led such conservative leaders as Klemens Wenzel, Prince von Metternich, to fear the rise of national sentiment.[19]
The assassination of German dramatist August von Kotzebue in March 1819 by a radical student seeking unification was followed on 20 September 1819 by the proclamation of the Carlsbad Decrees, which hampered intellectual leadership of the nationalist movement.[19] Metternich was able to harness conservative outrage at the assassination to consolidate legislation that would further limit the press and constrain the rising liberal and nationalist movements. Consequently, these decrees drove the Burschenschaften underground, restricted the publication of nationalist materials, expanded censorship of the press and private correspondence, and limited academic speech by prohibiting university professors from encouraging nationalist discussion. The decrees were the subject of Johann Joseph von Görres’s pamphlet Teutschland [archaic: Deutschland] und die Revolution (Germany and the Revolution) (1820), in which he concluded that it was both impossible and undesirable to repress the free utterance of public opinion by reactionary measures.[21]
The Hambach Festival (Hambacher Fest) in May 1832 was attended by a crowd of more than 30,000.[22] Promoted as a county fair,[23] its participants celebrated fraternity, liberty, and national unity. Celebrants gathered in the town below and marched to the ruins of Hambach Castle on the heights above the small town of Hambach, in the Palatinate province of Bavaria. Carrying flags, beating drums, and singing, the participants took the better part of the morning and mid-day to arrive at the castle grounds, where they listened to speeches by nationalist orators from across the conservative to radical political spectrum. The overall content of the speeches suggested a fundamental difference between the German nationalism of the 1830s and the French nationalism of the July Revolution: the focus of German nationalism lay in the education of the people; once the populace was educated as to what was needed, they would accomplish it. The Hambach rhetoric emphasized the overall peaceable nature of German nationalism: the point was not to build barricades, a very «French» form of nationalism, but to build emotional bridges between groups.[24] As he had done in 1819, after the Kotzebue assassination, Metternich used the popular demonstration at Hambach to push conservative social policy. The «Six Articles» of 28 June 1832 primarily reaffirmed the principle of monarchical authority. On 5 July, the Frankfurt Diet voted for an additional 10 articles, which reiterated existing rules on censorship, restricted political organizations, and limited other public activity. Furthermore, the member states agreed to send military assistance to any government threatened by unrest.[25] Prince Wrede led half of the Bavarian army to the Palatinate to «subdue» the province. Several hapless Hambach speakers were arrested, tried and imprisoned; one, Karl Heinrich Brüggemann (1810–1887), a law student and representative of the secretive Burschenschaft, was sent to Prussia, where he was first condemned to death, but later pardoned.[22]
Crucially, both the Wartburg rally in 1817 and the Hambach Festival in 1832 had lacked any clear-cut program of unification. At Hambach, the positions of the many speakers illustrated their disparate agendas. Held together only by the idea of unification, their notions of how to achieve this did not include specific plans but instead rested on the nebulous idea that the Volk (the people), if properly educated, would bring about unification on their own. Grand speeches, flags, exuberant students, and picnic lunches did not translate into a new political, bureaucratic, or administrative apparatus. While many spoke about the need for a constitution, no such document appeared from the discussions. In 1848, nationalists sought to remedy that problem.[26]
Economy and the customs union[edit]
This drawing offered a satirical commentary on the prevalence of toll barriers in the many German states, circa 1834. Some states were so small that transporters loaded and reloaded their cargoes two and three times a day.
Several other factors complicated the rise of nationalism in the German states. The man-made factors included political rivalries between members of the German confederation, particularly between the Austrians and the Prussians, and socio-economic competition among the commercial and merchant interests, and the old land-owning and aristocratic interests. Natural factors included widespread drought in the early 1830s, and again in the 1840s, and a food crisis in the 1840s. Further complications emerged as a result of a shift in industrialization and manufacturing; as people sought jobs, they left their villages and small towns to work during the week in the cities, returning for a day and a half on weekends.[27]
The economic, social and cultural dislocation of ordinary people, the economic hardship of an economy in transition, and the pressures of meteorological disasters all contributed to growing problems in Central Europe.[28] The failure of most of the governments to deal with the food crisis of the mid-1840s, caused by the potato blight (related to the Great Irish Famine) and several seasons of bad weather, encouraged many to think that the rich and powerful had no interest in their problems. Those in authority were concerned about the growing unrest, political and social agitation among the working classes, and the disaffection of the intelligentsia. No amount of censorship, fines, imprisonment, or banishment, it seemed, could stem the criticism. Furthermore, it was becoming increasingly clear that both Austria and Prussia wanted to be the leaders in any resulting unification; each would inhibit the drive of the other to achieve unification.[29]
Formation of the Zollverein, an institution key to unifying the German states economically, helped to create a larger sense of economic unification. Initially conceived by the Prussian Finance Minister Hans, Count von Bülow, as a Prussian customs union in 1818, the Zollverein linked the many Prussian and Hohenzollern territories. Over the ensuing thirty years (and more) other German states joined. The Union helped to reduce protectionist barriers between the German states, especially improving the transport of raw materials and finished goods, making it both easier to move goods across territorial borders and less costly to buy, transport, and sell raw materials. This was particularly important for the emerging industrial centers, most of which were located in the Prussian regions of the Rhineland, the Saar, and the Ruhr valleys.[30] States more distant from the coast joined the Customs Union earlier. Not being a member mattered more for the states of south Germany, since the external tariff of the Customs Union prevented customs-free access to the coast (which gave access to international markets). Thus, by 1836, all states to the south of Prussia had joined the Customs Union, except Austria.[31]
In contrast, the coastal states already had barrier free access to international trade and did not want consumers and producers burdened with the import duties they would pay if they were within the Zollverein customs border. Hanover on the north coast formed its own customs union – the “Tax Union” or Steuerverein – in 1834 with Brunswick and with Oldenburg in 1836. The external tariffs on finished goods and overseas raw materials were below the rates of the Zollverein. Brunswick joined the Zollverein Customs Union in 1842, while Hanover and Oldenburg finally joined in 1854[32] After the Austro-Prussian war of 1866, Schleswig, Holstein and Lauenburg were annexed by Prussia and thus annexed also to the Customs Union, while the two Mecklenburg states and the city states of Hamburg and Bremen joined late because they were reliant on international trade. The Mecklenburgs joined in 1867, while Bremen and Hamburg joined in 1888.[31]
Roads and railways[edit]
By the early 19th century, German roads had deteriorated to an appalling extent. Travelers, both foreign and local, complained bitterly about the state of the Heerstraßen, the military roads previously maintained for the ease of moving troops. As German states ceased to be a military crossroads, however, the roads improved; the length of hard–surfaced roads in Prussia increased from 3,800 kilometers (2,400 mi) in 1816 to 16,600 kilometers (10,300 mi) in 1852, helped in part by the invention of macadam. By 1835, Heinrich von Gagern wrote that roads were the «veins and arteries of the body politic…» and predicted that they would promote freedom, independence and prosperity.[33] As people moved around, they came into contact with others, on trains, at hotels, in restaurants, and for some, at fashionable resorts such as the spa in Baden-Baden. Water transportation also improved. The blockades on the Rhine had been removed by Napoleon’s orders, but by the 1820s, steam engines freed riverboats from the cumbersome system of men and animals that towed them upstream. By 1846, 180 steamers plied German rivers and Lake Constance, and a network of canals extended from the Danube, the Weser, and the Elbe rivers.[34]
As important as these improvements were, they could not compete with the impact of the railway. German economist Friedrich List called the railways and the Customs Union «Siamese Twins», emphasizing their important relationship to one another.[35] He was not alone: the poet August Heinrich Hoffmann von Fallersleben wrote a poem in which he extolled the virtues of the Zollverein, which he began with a list of commodities that had contributed more to German unity than politics or diplomacy.[36] Historians of the German Empire later regarded the railways as the first indicator of a unified state; the patriotic novelist, Wilhelm Raabe, wrote: «The German empire was founded with the construction of the first railway…»[37] Not everyone greeted the iron monster with enthusiasm. The Prussian king Frederick William III saw no advantage in traveling from Berlin to Potsdam a few hours faster, and Metternich refused to ride in one at all. Others wondered if the railways were an «evil» that threatened the landscape: Nikolaus Lenau’s 1838 poem An den Frühling (To Spring) bemoaned the way trains destroyed the pristine quietude of German forests.[38]
The Bavarian Ludwig Railway, which was the first passenger or freight rail line in the German lands, connected Nuremberg and Fürth in 1835. Although it was 6 kilometers (3.7 mi) long and only operated in daylight, it proved both profitable and popular. Within three years, 141 kilometers (88 mi) of track had been laid, by 1840, 462 kilometers (287 mi), and by 1860, 11,157 kilometers (6,933 mi). Lacking a geographically central organizing feature (such as a national capital), the rails were laid in webs, linking towns and markets within regions, regions within larger regions, and so on. As the rail network expanded, it became cheaper to transport goods: in 1840, 18 Pfennigs per ton per kilometer and in 1870, five Pfennigs. The effects of the railway were immediate. For example, raw materials could travel up and down the Ruhr Valley without having to unload and reload. Railway lines encouraged economic activity by creating demand for commodities and by facilitating commerce. In 1850, inland shipping carried three times more freight than railroads; by 1870, the situation was reversed, and railroads carried four times more. Rail travel changed how cities looked and how people traveled. Its impact reached throughout the social order, affecting the highest born to the lowest. Although some of the outlying German provinces were not serviced by rail until the 1890s, the majority of the population, manufacturing centers, and production centers were linked to the rail network by 1865.[39]
Geography, patriotism and language[edit]
German linguistic area (green) and political boundaries around 1841 (grey) in comparison to the text’s geographic references (bold blue)
As travel became easier, faster, and less expensive, Germans started to see unity in factors other than their language. The Brothers Grimm, who compiled a massive dictionary known as The Grimm, also assembled a compendium of folk tales and fables, which highlighted the story-telling parallels between different regions.[40] Karl Baedeker wrote guidebooks to different cities and regions of Central Europe, indicating places to stay, sites to visit, and giving a short history of castles, battlefields, famous buildings, and famous people. His guides also included distances, roads to avoid, and hiking paths to follow.[41]
The words of August Heinrich Hoffmann von Fallersleben expressed not only the linguistic unity of the German people but also their geographic unity. In Deutschland, Deutschland über Alles, officially called Das Lied der Deutschen («The Song of the Germans«), Fallersleben called upon sovereigns throughout the German states to recognize the unifying characteristics of the German people.[42] Such other patriotic songs as «Die Wacht am Rhein» («The Watch on the Rhine») by Max Schneckenburger began to focus attention on geographic space, not limiting «Germanness» to a common language. Schneckenburger wrote «The Watch on the Rhine» in a specific patriotic response to French assertions that the Rhine was France’s «natural» eastern boundary. In the refrain, «Dear fatherland, dear fatherland, put your mind to rest / The watch stands true on the Rhine», and in such other patriotic poetry as Nicholaus Becker’s «Das Rheinlied» («The Rhine»), Germans were called upon to defend their territorial homeland. In 1807, Alexander von Humboldt argued that national character reflected geographic influence, linking landscape to people. Concurrent with this idea, movements to preserve old fortresses and historic sites emerged, and these particularly focused on the Rhineland, the site of so many confrontations with France and Spain.[43]
German revolutions and Polish uprising of 1848–49[edit]
The widespread—mainly German—revolutions of 1848–49 sought unification of Germany under a single constitution. The revolutionaries pressured various state governments, particularly those in the Rhineland, for a parliamentary assembly that would have the responsibility to draft a constitution. Ultimately, many of the left-wing revolutionaries hoped this constitution would establish universal male suffrage, a permanent national parliament, and a unified Germany, possibly under the leadership of the Prussian king. This seemed to be the most logical course since Prussia was the strongest of the German states, as well as the largest in geographic size. Meanwhile, center-right revolutionaries sought some kind of expanded suffrage within their states and potentially, a form of loose unification. Finally, the Polish majority living in the share of Polish territory annexed by Prussia pursued their own liberation agenda.
Frankfurt Parliament[edit]
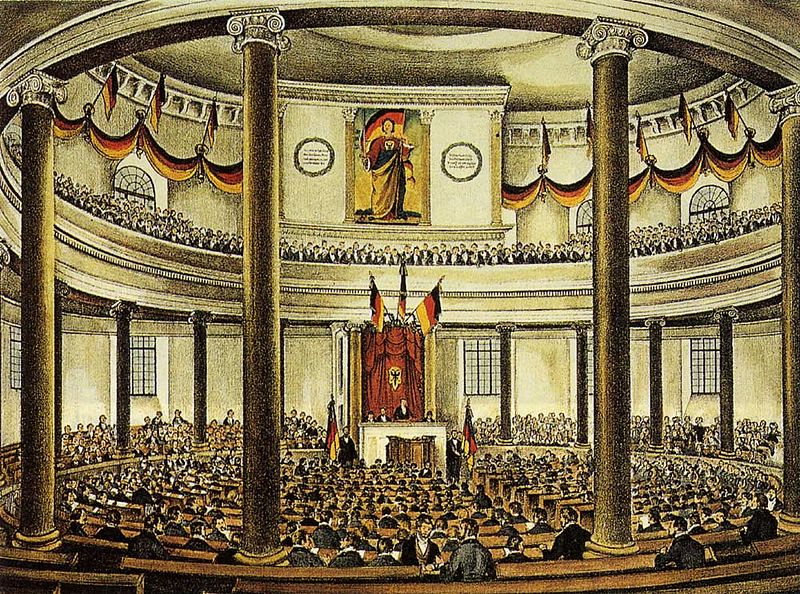
Pre-parliament delegates processing into Paul’s Church in Frankfurt, where they laid the groundwork for electing a National Parliament[44]
Their pressure resulted in a variety of elections, based on different voting qualifications, such as the Prussian three-class franchise, which granted to some electoral groups—chiefly the wealthier, landed ones—greater representative power.[45]
On 27 March 1849, the Frankfurt Parliament passed the Paulskirchenverfassung (Constitution of St. Paul’s Church) and offered the title of Kaiser (Emperor) to the Prussian king Frederick William IV the next month. He refused for a variety of reasons. Publicly, he replied that he could not accept a crown without the consent of the actual states, by which he meant the princes. Privately, he feared opposition from the other German princes and military intervention from Austria or Russia. He also held a fundamental distaste for the idea of accepting a crown from a popularly elected parliament: he would not accept a crown of «clay».[46] Despite franchise requirements that often perpetuated many of the problems of sovereignty and political participation liberals sought to overcome, the Frankfurt Parliament did manage to draft a constitution and reach an agreement on the kleindeutsch solution. While the liberals failed to achieve the unification they sought, they did manage to gain a partial victory by working with the German princes on many constitutional issues and collaborating with them on reforms.[47]
The aborted 1848–49 German Empire in retrospective analysis[edit]
Scholars of German history have engaged in decades of debate over how the successes and failures of the Frankfurt Parliament contribute to the historiographical explanations of German nation building. One school of thought, which emerged after The Great War and gained momentum in the aftermath of World War II, maintains that the failure of German liberals in the Frankfurt Parliament led to bourgeoisie compromise with conservatives (especially the conservative Junker landholders), which subsequently led to the so-called Sonderweg (distinctive path) of 20th-century German history.[48] Failure to achieve unification in 1848, this argument holds, resulted in the late formation of the nation-state in 1871, which in turn delayed the development of positive national values. Hitler often called on the German public to sacrifice all for the cause of their great nation, but his regime did not create German nationalism: it merely capitalized on an intrinsic cultural value of German society that still remains prevalent even to this day.[49] Furthermore, this argument maintains, the «failure» of 1848 reaffirmed latent aristocratic longings among the German middle class; consequently, this group never developed a self-conscious program of modernization.[50]
More recent scholarship has rejected this idea, claiming that Germany did not have an actual «distinctive path» any more than any other nation, a historiographic idea known as exceptionalism.[51] Instead, modern historians claim 1848 saw specific achievements by the liberal politicians. Many of their ideas and programs were later incorporated into Bismarck’s social programs (e.g., social insurance, education programs, and wider definitions of suffrage). In addition, the notion of a distinctive path relies upon the underlying assumption that some other nation’s path (in this case, the United Kingdom’s) is the accepted norm.[52] This new argument further challenges the norms of the British-centric model of development: studies of national development in Britain and other «normal» states (e.g., France or the United States) have suggested that even in these cases, the modern nation-state did not develop evenly. Nor did it develop particularly early, being rather a largely mid-to-late-19th-century phenomenon.[53] Since the end of the 1990s, this view has become widely accepted, although some historians still find the Sonderweg analysis helpful in understanding the period of National Socialism.[54][55]
Problem of spheres of influence: The Erfurt Union and the Punctation of Olmütz[edit]
This depiction of Germania, also by Philipp Veit, was created to hide the organ of the Paul’s Church in Frankfurt, during the meeting of the Parliament there, March 1848–49. The sword was intended to symbolize the Word of God and to mark the renewal of the people and their triumphant spirit.
After the Frankfurt Parliament disbanded, Frederick William IV, under the influence of General Joseph Maria von Radowitz, supported the establishment of the Erfurt Union—a federation of German states, excluding Austria—by the free agreement of the German princes. This limited union under Prussia would have almost eliminated Austrian influence on the other German states. Combined diplomatic pressure from Austria and Russia (a guarantor of the 1815 agreements that established European spheres of influence) forced Prussia to relinquish the idea of the Erfurt Union at a meeting in the small town of Olmütz in Moravia. In November 1850, the Prussians—specifically Radowitz and Frederick William—agreed to the restoration of the German Confederation under Austrian leadership. This became known as the Punctation of Olmütz, but among Prussians it was known as the «Humiliation of Olmütz.»[56]
Although seemingly minor events, the Erfurt Union proposal and the Punctation of Olmütz brought the problems of influence in the German states into sharp focus. The question became not a matter of if but rather when unification would occur, and when was contingent upon strength. One of the former Frankfurt Parliament members, Johann Gustav Droysen, summed up the problem:
We cannot conceal the fact that the whole German question is a simple alternative between Prussia and Austria. In these states, German life has its positive and negative poles—in the former, all the interests [that] are national and reformative, in the latter, all that are dynastic and destructive. The German question is not a constitutional question but a question of power; and the Prussian monarchy is now wholly German, while that of Austria cannot be.[57]
Unification under these conditions raised a basic diplomatic problem. The possibility of German (or Italian) unification would overturn the overlapping spheres of influence system created in 1815 at the Congress of Vienna. The principal architects of this convention, Metternich, Castlereagh, and Tsar Alexander (with his foreign secretary Count Karl Nesselrode), had conceived of and organized a Europe balanced and guaranteed by four «great powers»: Great Britain, France, Russia, and Austria, with each power having a geographic sphere of influence. France’s sphere included the Iberian Peninsula and a share of influence in the Italian states. Russia’s included the eastern regions of Central Europe and a balancing influence in the Balkans. Austria’s sphere expanded throughout much of the Central European territories formerly held by the Holy Roman Empire. Britain’s sphere was the rest of the world, especially the seas.[58]
This sphere of influence system depended upon the fragmentation of the German and Italian states, not their consolidation. Consequently, a German nation united under one banner presented significant questions. There was no readily applicable definition for who the German people would be or how far the borders of a German nation would stretch. There was also uncertainty as to who would best lead and defend «Germany», however it was defined. Different groups offered different solutions to this problem. In the Kleindeutschland («Lesser Germany») solution, the German states would be united under the leadership of the Prussian Hohenzollerns; in the Grossdeutschland («Greater Germany») solution, the German states would be united under the leadership of the Austrian Habsburgs. This controversy, the latest phase of the German dualism debate that had dominated the politics of the German states and Austro-Prussian diplomacy since the 1701 creation of the Kingdom of Prussia, would come to a head during the following twenty years.[59]
External expectations of a unified Germany[edit]
Other nationalists had high hopes for the German unification movement, and the frustration with lasting German unification after 1850 seemed to set the national movement back. Revolutionaries associated national unification with progress. As Giuseppe Garibaldi wrote to German revolutionary Karl Blind on 10 April 1865, «The progress of humanity seems to have come to a halt, and you with your superior intelligence will know why. The reason is that the world lacks a nation [that] possesses true leadership. Such leadership, of course, is required not to dominate other peoples but to lead them along the path of duty, to lead them toward the brotherhood of nations where all the barriers erected by egoism will be destroyed.» Garibaldi looked to Germany for the «kind of leadership [that], in the true tradition of medieval chivalry, would devote itself to redressing wrongs, supporting the weak, sacrificing momentary gains and material advantage for the much finer and more satisfying achievement of relieving the suffering of our fellow men. We need a nation courageous enough to give us a lead in this direction. It would rally to its cause all those who are suffering wrong or who aspire to a better life and all those who are now enduring foreign oppression.»
[60]
German unification had also been viewed as a prerequisite for the creation of a European federation, which Giuseppe Mazzini and other European patriots had been promoting for more than three decades:
In the spring of 1834, while at Berne, Mazzini and a dozen refugees from Italy, Poland and Germany founded a new association with the grandiose name of Young Europe. Its basic, and equally grandiose idea, was that, as the French Revolution of 1789 had enlarged the concept of individual liberty, another revolution would now be needed for national liberty; and his vision went further because he hoped that in the no doubt distant future free nations might combine to form a loosely federal Europe with some kind of federal assembly to regulate their common interests. […] His intention was nothing less than to overturn the European settlement agreed [to] in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna, which had reestablished an oppressive hegemony of a few great powers and blocked the emergence of smaller nations. […] Mazzini hoped, but without much confidence, that his vision of a league or society of independent nations would be realized in his own lifetime. In practice Young Europe lacked the money and popular support for more than a short-term existence. Nevertheless he always remained faithful to the ideal of a united continent for which the creation of individual nations would be an indispensable preliminary.[61]
Prussia’s growing strength: Realpolitik[edit]
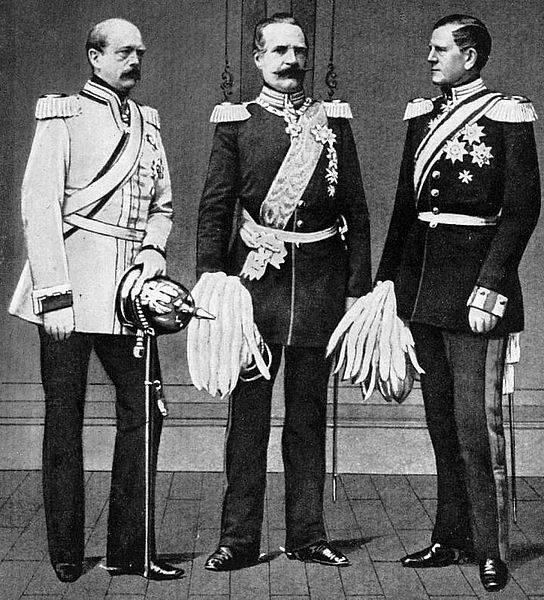
The convergence of leadership in politics and diplomacy by Bismarck, left, reorganization of the army and its training techniques by Albrecht von Roon (center), and the redesign of operational and strategic principles by Helmuth von Moltke (right) placed Prussia among the most powerful states in European affairs after the 1860s.
King Frederick William IV suffered a stroke in 1857 and could no longer rule. This led to his brother William becoming prince regent of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1858. Meanwhile, Helmuth von Moltke had become chief of the Prussian General Staff in 1857, and Albrecht von Roon would become Prussian Minister of War in 1859.[62] This shuffling of authority within the Prussian military establishment would have important consequences. Von Roon and William (who took an active interest in military structures) began reorganizing the Prussian army, while Moltke redesigned the strategic defense of Prussia by streamlining operational command. Prussian army reforms (especially how to pay for them) caused a constitutional crisis beginning in 1860 because both parliament and William—via his minister of war—wanted control over the military budget. William, crowned King Wilhelm I in 1861, appointed Otto von Bismarck to the position of Minister-President of Prussia in 1862. Bismarck resolved the crisis in favor of the war minister.[63]
The Crimean War of 1854–55 and the Italian War of 1859 disrupted relations among Great Britain, France, Austria, and Russia. In the aftermath of this disarray, the convergence of von Moltke’s operational redesign, von Roon and Wilhelm’s army restructure, and Bismarck’s diplomacy influenced the realignment of the European balance of power. Their combined agendas established Prussia as the leading German power through a combination of foreign diplomatic triumphs—backed up by the possible use of Prussian military might—and an internal conservatism tempered by pragmatism, which came to be known as Realpolitik.[64]
Bismarck expressed the essence of Realpolitik in his subsequently famous «Blood and Iron» speech to the Budget Committee of the Prussian Chamber of Deputies on 30 September 1862, shortly after he became Minister President: «The great questions of the time will not be resolved by speeches and majority decisions—that was the great mistake of 1848 and 1849—but by iron and blood.»[65] Bismarck’s words, «iron and blood» (or «blood and iron», as often attributed), have often been misappropriated as evidence of a German lust for blood and power.[66] First, the phrase from his speech «the great questions of time will not be resolved by speeches and majority decisions» is often interpreted as a repudiation of the political process—a repudiation Bismarck did not himself advocate.[67] Second, his emphasis on blood and iron did not imply simply the unrivaled military might of the Prussian army but rather two important aspects: the ability of the assorted German states to produce iron and other related war materials and the willingness to use those war materials if necessary.[68]
By 1862, when Bismarck made his speech, the idea of a German nation-state in the peaceful spirit of Pan-Germanism had shifted from the liberal and democratic character of 1848 to accommodate Bismarck’s more conservative Realpolitik. Bismarck sought to link a unified state to the Hohenzollern dynasty, which for some historians remains one of Bismarck’s primary contributions to the creation of the German Empire in 1871.[69] While the conditions of the treaties binding the various German states to one another prohibited Bismarck from taking unilateral action, the politician and diplomat in him realized the impracticality of this.[70] To get the German states to unify, Bismarck needed a single, outside enemy that would declare war on one of the German states first, thus providing a casus belli to rally all Germans behind. This opportunity arose with the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. Historians have long debated Bismarck’s role in the events leading up to the war. The traditional view, promulgated in large part by late 19th- and early 20th-century pro-Prussian historians, maintains that Bismarck’s intent was always German unification. Post-1945 historians, however, see more short-term opportunism and cynicism in Bismarck’s manipulation of the circumstances to create a war, rather than a grand scheme to unify a nation-state.[71] Regardless of motivation, by manipulating events of 1866 and 1870, Bismarck demonstrated the political and diplomatic skill that had caused Wilhelm to turn to him in 1862.[72]
Three episodes proved fundamental to the unification of Germany. First, the death without male heirs of Frederick VII of Denmark led to the Second War of Schleswig in 1864. Second, the unification of Italy provided Prussia an ally against Austria in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866. Finally, France—fearing Hohenzollern encirclement—declared war on Prussia in 1870, resulting in the Franco-Prussian War. Through a combination of Bismarck’s diplomacy and political leadership, von Roon’s military reorganization, and von Moltke’s military strategy, Prussia demonstrated that none of the European signatories of the 1815 peace treaty could guarantee Austria’s sphere of influence in Central Europe, thus achieving Prussian hegemony in Germany and ending the dualism debate.[73]
The Schleswig-Holstein Question[edit]
The first episode in the saga of German unification under Bismarck came with the Schleswig-Holstein Question. On 15 November 1863, Christian IX became king of Denmark and duke of Schleswig, Holstein, and Lauenburg, which the Danish king held in personal union. On 18 November 1863, he signed the Danish November Constitution which replaced The Law of Sjælland and The Law of Jutland, which meant the new constitution applied to the Duchy of Schleswig. The German Confederation saw this act as a violation of the London Protocol of 1852, which emphasized the status of the Kingdom of Denmark as distinct from the three independent duchies. The German Confederation could use the ethnicities of the area as a rallying cry: Holstein and Lauenburg were largely of German origin and spoke German in everyday life, while Schleswig had a significant Danish population and history. Diplomatic attempts to have the November Constitution repealed collapsed, and fighting began when Prussian and Austrian troops crossed the Eider river on 1 February 1864.
Initially, the Danes attempted to defend their country using an ancient earthen wall known as the Danevirke, but this proved futile. The Danes were no match for the combined Prussian and Austrian forces and their modern armaments. The needle gun, one of the first bolt action rifles to be used in conflict, aided the Prussians in both this war and the Austro-Prussian War two years later. The rifle enabled a Prussian soldier to fire five shots while lying prone, while its muzzle-loading counterpart could only fire one shot and had to be reloaded while standing. The Second Schleswig War resulted in victory for the combined armies of Prussia and Austria, and the two countries won control of Schleswig and Holstein in the concluding peace of Vienna, signed on 30 October 1864.[74]
War between Austria and Prussia, 1866[edit]
Situation at the time of the outbreak of the war:
Prussia
Austria
Austria’s allies
Prussia’s allies
Neutral
Under joint administration (Schleswig-Holstein)
The second episode in Bismarck’s unification efforts occurred in 1866. In concert with the newly formed Italy, Bismarck created a diplomatic environment in which Austria declared war on Prussia. The dramatic prelude to the war occurred largely in Frankfurt, where the two powers claimed to speak for all the German states in the parliament. In April 1866, the Prussian representative in Florence signed a secret agreement with the Italian government, committing each state to assist the other in a war against Austria. The next day, the Prussian delegate to the Frankfurt assembly presented a plan calling for a national constitution, a directly elected national Diet, and universal suffrage. German liberals were justifiably skeptical of this plan, having witnessed Bismarck’s difficult and ambiguous relationship with the Prussian Landtag (State Parliament), a relationship characterized by Bismarck’s cajoling and riding roughshod over the representatives. These skeptics saw the proposal as a ploy to enhance Prussian power rather than a progressive agenda of reform.[75]
Choosing sides[edit]
The debate over the proposed national constitution became moot when news of Italian troop movements in Tyrol and near the Venetian border reached Vienna in April 1866. The Austrian government ordered partial mobilization in the southern regions; the Italians responded by ordering full mobilization. Despite calls for rational thought and action, Italy, Prussia, and Austria continued to rush toward armed conflict. On 1 May, Wilhelm gave von Moltke command over the Prussian armed forces, and the next day he began full-scale mobilization.[76]
In the Diet, the group of middle-sized states, known as Mittelstaaten (Bavaria, Württemberg, the grand duchies of Baden and Hesse, and the duchies of Saxony–Weimar, Saxony–Meiningen, Saxony–Coburg, and Nassau), supported complete demobilization within the Confederation. These individual governments rejected the potent combination of enticing promises and subtle (or outright) threats Bismarck used to try to gain their support against the Habsburgs. The Prussian war cabinet understood that its only supporters among the German states against the Habsburgs were two small principalities bordering on Brandenburg that had little military strength or political clout: the Grand Duchies of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz. They also understood that Prussia’s only ally abroad was Italy.[77]
Opposition to Prussia’s strong-armed tactics surfaced in other social and political groups. Throughout the German states, city councils, liberal parliamentary members who favored a unified state, and chambers of commerce—which would see great benefits from unification—opposed any war between Prussia and Austria. They believed any such conflict would only serve the interests of royal dynasties. Their own interests, which they understood as «civil» or «bourgeois», seemed irrelevant. Public opinion also opposed Prussian domination. Catholic populations along the Rhine—especially in such cosmopolitan regions as Cologne and in the heavily populated Ruhr Valley—continued to support Austria. By late spring, most important states opposed Berlin’s effort to reorganize the German states by force. The Prussian cabinet saw German unity as an issue of power and a question of who had the strength and will to wield that power. Meanwhile, the liberals in the Frankfurt assembly saw German unity as a process of negotiation that would lead to the distribution of power among the many parties.[78]
Austria isolated[edit]
Although several German states initially sided with Austria, they stayed on the defensive and failed to take effective initiatives against Prussian troops. The Austrian army therefore faced the technologically superior Prussian army with support only from Saxony. France promised aid, but it came late and was insufficient.[79] Complicating the situation for Austria, the Italian mobilization on Austria’s southern border required a diversion of forces away from battle with Prussia to fight the Third Italian War of Independence on a second front in Venetia and on the Adriatic sea.[80]
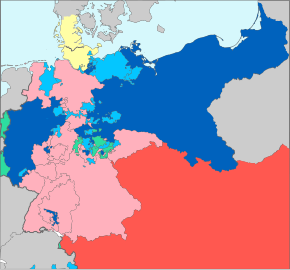
Aftermath of the war:
Prussia
Territories annexed by Prussia
Prussia’s allies
Austria
Austria’s allies
Neutral members of the German Confederation
A quick peace was essential to keep Russia from entering the conflict on Austria’s side.[81] In the day-long Battle of Königgrätz, near the village of Sadová, Friedrich Carl and his troops arrived late, and in the wrong place. Once he arrived, however, he ordered his troops immediately into the fray. The battle was a decisive victory for Prussia and forced the Habsburgs to end the war with the unfavorable Peace of Prague,[82] laying the groundwork for the Kleindeutschland (little Germany) solution, or «Germany without Austria.»
Founding a unified state[edit]
There is, in political geography, no Germany proper to speak of. There are Kingdoms and Grand Duchies, and Duchies and Principalities, inhabited by Germans, and each [is] separately ruled by an independent sovereign with all the machinery of State. Yet there is a natural undercurrent tending to a national feeling and toward a union of the Germans into one great nation, ruled by one common head as a national unit.
Peace of Prague and the North German Confederation[edit]
The Peace of Prague sealed the dissolution of the German Confederation. Its former leading state, the Austrian Empire, was along with the majority of its allies excluded from the ensuing North German Confederation Treaty sponsored by Prussia which directly annexed Hanover, Hesse-Kassel, Nassau, and the city of Frankfurt, while Hesse Darmstadt lost some territory but kept its statehood. At the same time, the original East Prussian craddle of the Prussian statehood as well as the Prussian-held Polish- or Kashubian-speaking territories of Province of Posen and West Prussia were formally annexed into the North German Confederation, thus Germany. Following adoption of the North German Constitution, the new state obtained its own constitution, flag, and governmental and administrative structures.
Through military victory, Prussia under Bismarck’s influence had overcome Austria’s active resistance to the idea of a unified Germany. The states south of the Main River (Baden, Württemberg, and Bavaria) signed separate treaties requiring them to pay indemnities and to form alliances bringing them into Prussia’s sphere of influence.[84] Austria’s influence over the German states may have been broken, but the war also splintered the spirit of pan-German unity, as many German states resented Prussian power politics.[85]
Unified Italy and Austro-Hungarian Compromise[edit]
The Peace of Prague offered lenient terms to Austria but its relationship with the new nation-state of Italy underwent major restructuring. Although the Austrians were far more successful in the military field against Italian troops, the monarchy lost the important province of Venetia. The Habsburgs ceded Venetia to France, which then formally transferred control to Italy.[86]
The end of Austrian dominance of the German states shifted Austria’s attention to the Balkans. The reality of defeat for Austria also caused a reevaluation of internal divisions, local autonomy, and liberalism.[87] In 1867, the Austrian emperor Franz Joseph accepted a settlement (the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867) in which he gave his Hungarian holdings equal status with his Austrian domains, creating the Dual Monarchy of Austria-Hungary.[88]
War with France[edit]
The French public resented the Prussian victory and demanded Revanche pour Sadová («Revenge for Sadova»), illustrating anti-Prussian sentiment in France—a problem that would accelerate in the months leading up to the Franco-Prussian War.[89] The Austro-Prussian War also damaged relations with the French government. At a meeting in Biarritz in September 1865 with Napoleon III, Bismarck had let it be understood (or Napoleon had thought he understood) that France might annex parts of Belgium and Luxembourg in exchange for its neutrality in the war. These annexations did not happen, resulting in animosity from Napoleon towards Bismarck.
Background[edit]
By 1870 three of the important lessons of the Austro-Prussian war had become apparent. The first lesson was that, through force of arms, a powerful state could challenge the old alliances and spheres of influence established in 1815. Second, through diplomatic maneuvering, a skilful leader could create an environment in which a rival state would declare war first, thus forcing states allied with the «victim» of external aggression to come to the leader’s aid. Finally, as Prussian military capacity far exceeded that of Austria, Prussia was clearly the only state within the Confederation (or among the German states generally) capable of protecting all of them from potential interference or aggression. In 1866, most mid-sized German states had opposed Prussia, but by 1870 these states had been coerced and coaxed into mutually protective alliances with Prussia. If a European state declared war on one of their members, then they all would come to the defense of the attacked state. With skilful manipulation of European politics, Bismarck created a situation in which France would play the role of aggressor in German affairs, while Prussia would play that of the protector of German rights and liberties.[90]
At the Congress of Vienna in 1815, Metternich and his conservative allies had reestablished the Spanish monarchy under King Ferdinand VII. Over the following forty years, the great powers supported the Spanish monarchy, but events in 1868 would further test the old system, finally providing the external trigger needed by Bismarck.
Spanish prelude[edit]
A revolution in Spain overthrew Queen Isabella II, and the throne remained empty while Isabella lived in sumptuous exile in Paris. The Spanish, looking for a suitable Catholic successor, had offered the post to three European princes, each of whom was rejected by Napoleon III, who served as regional power-broker.
Finally, in 1870 the Regency offered the crown to Leopold of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, a prince of the Catholic cadet Hohenzollern line. The ensuing furor has been dubbed by historians as the Hohenzollern candidature.[91] Over the next few weeks, the Spanish offer turned into the talk of Europe. Bismarck encouraged Leopold to accept the offer.[92] A successful installment of a Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen king in Spain would mean that two countries on either side of France would both have German kings of Hohenzollern descent. This may have been a pleasing prospect for Bismarck, but it was unacceptable to either Napoleon III or to Agenor, duc de Gramont, his minister of foreign affairs. Gramont wrote a sharply formulated ultimatum to Wilhelm, as head of the Hohenzollern family, stating that if any Hohenzollern prince should accept the crown of Spain, the French government would respond—although he left ambiguous the nature of such response. The prince withdrew as a candidate, thus defusing the crisis, but the French ambassador to Berlin would not let the issue lie.[93] He approached the Prussian king directly while Wilhelm was vacationing in Ems Spa, demanding that the King release a statement saying he would never support the installation of a Hohenzollern on the throne of Spain. Wilhelm refused to give such an encompassing statement, and he sent Bismarck a dispatch by telegram describing the French demands. Bismarck used the king’s telegram, called the Ems Dispatch, as a template for a short statement to the press. With its wording shortened and sharpened by Bismarck—and further alterations made in the course of its translation by the French agency Havas—the Ems Dispatch raised an angry furor in France. The French public, still aggravated over the defeat at Sadová, demanded war.[94]
Open hostilities and the disastrous end of the Second French Empire[edit]
Emperor Napoleon III (left) at Sedan, on 2 September 1870, seated next to Prussian Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, holding Napoleon’s surrendered sword. The defeat of the French army destabilized Napoleon’s regime; a revolution in Paris established the Third French Republic, and the war continued.
Napoleon III had tried to secure territorial concessions from both sides before and after the Austro-Prussian War, but despite his role as mediator during the peace negotiations, he ended up with nothing. He then hoped that Austria would join in a war of revenge and that its former allies—particularly the southern German states of Baden, Württemberg, and Bavaria—would join in the cause. This hope would prove futile since the 1866 treaty came into effect and united all German states militarily—if not happily—to fight against France. Instead of a war of revenge against Prussia, supported by various German allies, France engaged in a war against all of the German states without any allies of its own.[95]
The reorganization of the military by von Roon and the operational strategy of Moltke combined against France to great effect. The speed of Prussian mobilization astonished the French, and the Prussian ability to concentrate power at specific points—reminiscent of Napoleon I’s strategies seventy years earlier—overwhelmed French mobilization. Utilizing their efficiently laid rail grid, Prussian troops were delivered to battle areas rested and prepared to fight, whereas French troops had to march for considerable distances to reach combat zones. After a number of battles, notably Spicheren, Wörth, Mars la Tour, and Gravelotte, the Prussians defeated the main French armies and advanced on the primary city of Metz and the French capital of Paris. They captured Napoleon III and took an entire army as prisoners at Sedan on 1 September 1870.[96]
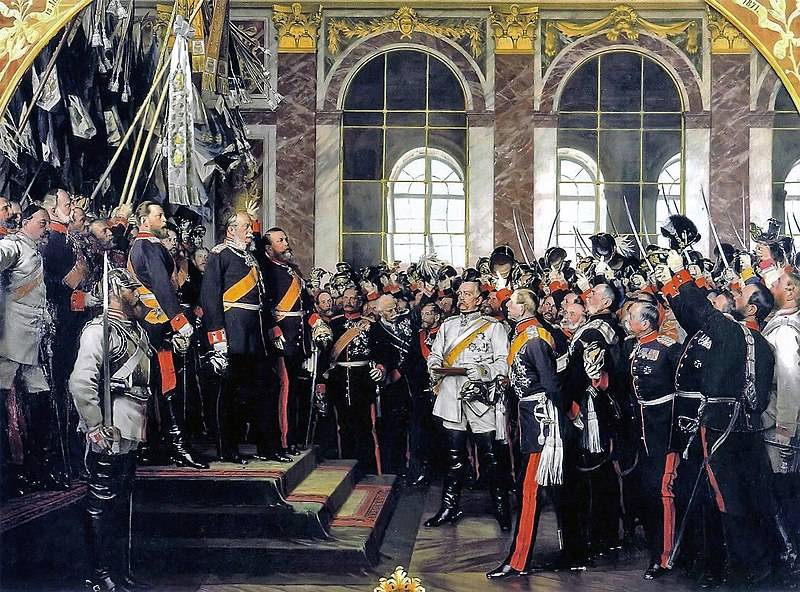
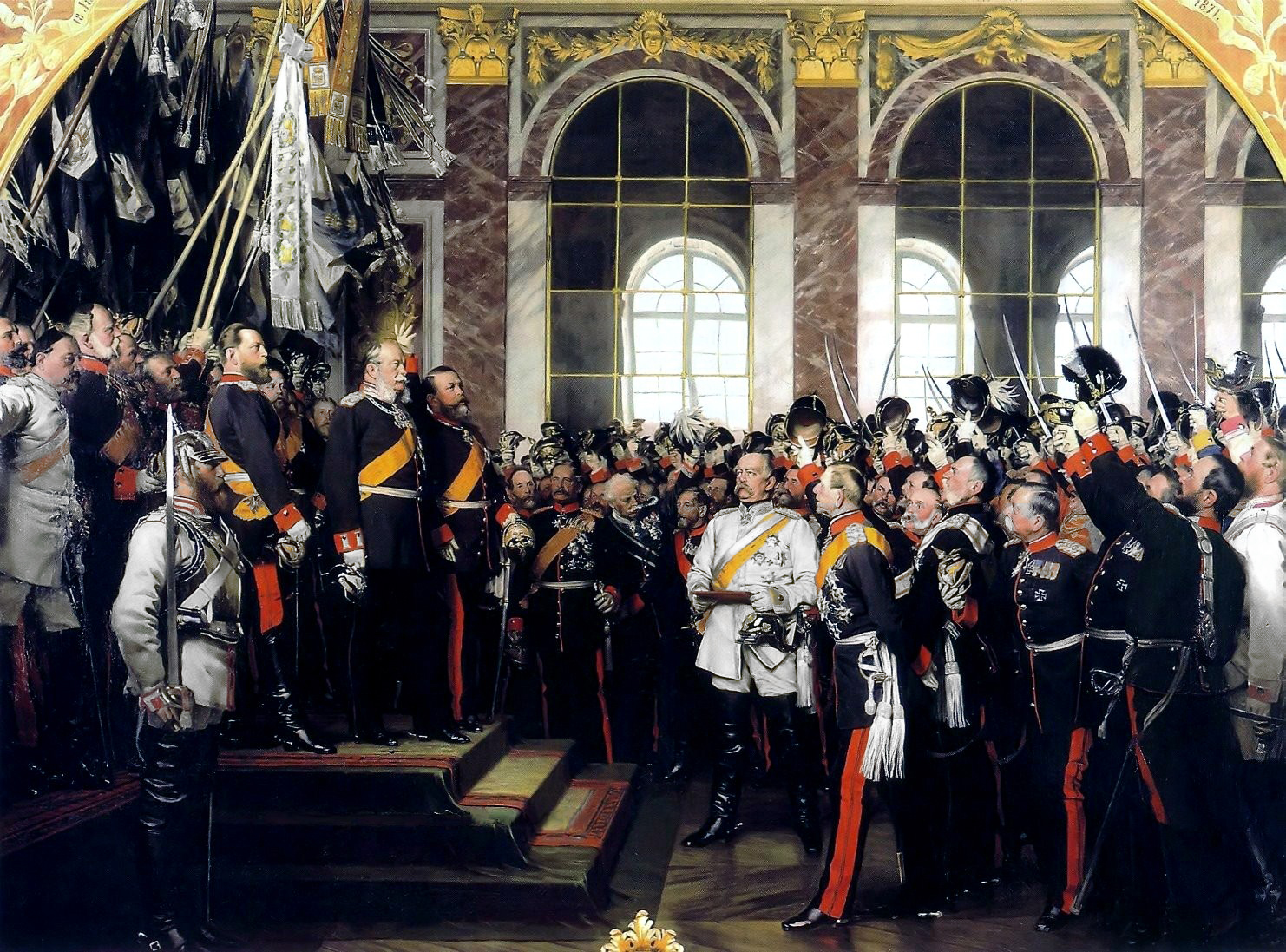
Proclamation of the German Empire[edit]
The humiliating capture of the French emperor and the loss of the French army itself, which marched into captivity at a makeshift camp in the Saarland («Camp Misery»), threw the French government into turmoil; Napoleon’s energetic opponents overthrew his government and proclaimed the Third Republic.[97] «In the days after Sedan, Prussian envoys met with the French and demanded a large cash indemnity as well as the cession of Alsace and Lorraine. All parties in France rejected the terms, insisting that any armistice be forged “on the basis of territorial integrity.” France, in other words, would pay reparations for starting the war, but would, in Jules Favre’s famous phrase, “cede neither a clod of our earth nor a stone of our fortresses».[98] The German High Command expected an overture of peace from the French, but the new republic refused to surrender. The Prussian army invested Paris and held it under siege until mid-January, with the city being «ineffectually bombarded».[99] Nevertheless, in January, the Germans fired some 12,000 shells, 300–400 grenades daily into the city.[100] On January 18, 1871, the German princes and senior military commanders proclaimed Wilhelm «German Emperor» in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles.[101] Under the subsequent Treaty of Frankfurt, France relinquished most of its traditionally German regions (Alsace and the German-speaking part of Lorraine); paid an indemnity, calculated (on the basis of population) as the precise equivalent of the indemnity that Napoleon Bonaparte imposed on Prussia in 1807;[102] and accepted German administration of Paris and most of northern France, with «German troops to be withdrawn stage by stage with each installment of the indemnity payment».[103]
War as ″the capstone of the unification process″[edit]
Victory in the Franco-Prussian War proved the capstone of the unification process. In the first half of the 1860s, Austria and Prussia both contended to speak for the German states; both maintained they could support German interests abroad and protect German interests at home. In responding to the Schleswig-Holstein Question, they both proved equally diligent in doing so. After the victory over Austria in 1866, Prussia began internally asserting its authority to speak for the German states and defend German interests, while Austria began directing more and more of its attention to possessions in the Balkans. The victory over France in 1871 expanded Prussian hegemony in the German states (aside from Austria) to the international level. With the proclamation of Wilhelm as Kaiser, Prussia assumed the leadership of the new empire. The southern states became officially incorporated into a unified Germany at the Treaty of Versailles of 1871 (signed 26 February 1871; later ratified in the Treaty of Frankfurt of 10 May 1871), which formally ended the war.[104] Although Bismarck had led the transformation of Germany from a loose confederation into a federal nation state, he had not done it alone. Unification was achieved by building on a tradition of legal collaboration under the Holy Roman Empire and economic collaboration through the Zollverein. The difficulties of the Vormärz, the impact of the 1848 liberals, the importance of von Roon’s military reorganization, and von Moltke’s strategic brilliance all played a part in political unification.[105] «Einheit – unity – was achieved at the expense of Freiheit – freedom. The German Empire became,» in Karl Marx’s words, “a military despotism cloaked in parliamentary forms with a feudal ingredient, influenced by the bourgeoisie, festooned with bureaucrats and guarded by police.” Indeed, many historians would see Germany’s “escape into war” in 1914 as a flight from all of the internal-political contradictions forged by Bismarck at Versailles in the fall of 1870.[106]
Internal political and administrative unification[edit]
The new German Empire included 26 political entities: twenty-five constituent states (or Bundesstaaten) and one Imperial Territory (or Reichsland). It realized the Kleindeutsche Lösung («Lesser German Solution», with the exclusion of Austria) as opposed to a Großdeutsche Lösung or «Greater German Solution», which would have included Austria. Unifying various states into one nation required more than some military victories, however much these might have boosted morale. It also required a rethinking of political, social, and cultural behaviors and the construction of new metaphors about «us» and «them». Who were the new members of this new nation? What did they stand for? How were they to be organized?[107]
Constituent states of the Empire[edit]
Though often characterized as a federation of monarchs, the German Empire, strictly speaking, federated a group of 26 constituent entities with different forms of government, ranging from the main four constitutional monarchies to the three republican Hanseatic cities.[108]
|
|
|
Political structure of the Empire[edit]
The 1866 North German Constitution became (with some semantic adjustments) the 1871 Constitution of the German Empire. With this constitution, the new Germany acquired some democratic features: notably the Imperial Diet, which—in contrast to the parliament of Prussia—gave citizens representation on the basis of elections by direct and equal suffrage of all males who had reached the age of 25. Furthermore, elections were generally free of chicanery, engendering pride in the national parliament.[109] However, legislation required the consent of the Bundesrat, the federal council of deputies from the states, in and over which Prussia had a powerful influence; Prussia could appoint 17 of 58 delegates with only 14 votes needed for a veto. Prussia thus exercised influence in both bodies, with executive power vested in the Prussian King as Kaiser, who appointed the federal chancellor. The chancellor was accountable solely to, and served entirely at the discretion of, the Emperor. Officially, the chancellor functioned as a one-man cabinet and was responsible for the conduct of all state affairs; in practice, the State Secretaries (bureaucratic top officials in charge of such fields as finance, war, foreign affairs, etc.) acted as unofficial portfolio ministers. With the exception of the years 1872–1873 and 1892–1894, the imperial chancellor was always simultaneously the prime minister of the imperial dynasty’s hegemonic home-kingdom, Prussia. The Imperial Diet had the power to pass, amend, or reject bills, but it could not initiate legislation. (The power of initiating legislation rested with the chancellor.) The other states retained their own governments, but the military forces of the smaller states came under Prussian control. The militaries of the larger states (such as the Kingdoms of Bavaria and Saxony) retained some autonomy, but they underwent major reforms to coordinate with Prussian military principles and came under federal government control in wartime.[110]
Historical arguments and the Empire’s social anatomy[edit]
The Sonderweg hypothesis attributed Germany’s difficult 20th century to the weak political, legal, and economic basis of the new empire. The Prussian landed elites, the Junkers, retained a substantial share of political power in the unified state. The Sonderweg hypothesis attributed their power to the absence of a revolutionary breakthrough by the middle classes, or by peasants in combination with the urban workers, in 1848 and again in 1871. Recent research into the role of the Grand Bourgeoisie—which included bankers, merchants, industrialists, and entrepreneurs—in the construction of the new state has largely refuted the claim of political and economic dominance of the Junkers as a social group. This newer scholarship has demonstrated the importance of the merchant classes of the Hanseatic cities and the industrial leadership (the latter particularly important in the Rhineland) in the ongoing development of the Second Empire.[111]
Additional studies of different groups in Wilhelmine Germany have all contributed to a new view of the period. Although the Junkers did, indeed, continue to control the officer corps, they did not dominate social, political, and economic matters as much as the Sonderweg theorists had hypothesized. Eastern Junker power had a counterweight in the western provinces in the form of the Grand Bourgeoisie and in the growing professional class of bureaucrats, teachers, professors, doctors, lawyers, scientists, etc.[112]
Beyond the political mechanism: forming a nation[edit]
If the Wartburg and Hambach rallies had lacked a constitution and administrative apparatus, that problem was addressed between 1867 and 1871. Yet, as Germans discovered, grand speeches, flags, and enthusiastic crowds, a constitution, a political reorganization, and the provision of an imperial superstructure; and the revised Customs Union of 1867–68, still did not make a nation.[113]
A key element of the nation-state is the creation of a national culture, frequently—although not necessarily—through deliberate national policy.[114] In the new German nation, a Kulturkampf (1872–78) that followed political, economic, and administrative unification attempted to address, with a remarkable lack of success, some of the contradictions in German society. In particular, it involved a struggle over language, education, and religion. A policy of Germanization of non-German people of the empire’s population, including the Polish and Danish minorities, started with language, in particular, the German language, compulsory schooling (Germanization), and the attempted creation of standardized curricula for those schools to promote and celebrate the idea of a shared past. Finally, it extended to the religion of the new Empire’s population.[115]
Kulturkampf[edit]
For some Germans, the definition of nation did not include pluralism, and Catholics in particular came under scrutiny; some Germans, and especially Bismarck, feared that the Catholics’ connection to the papacy might make them less loyal to the nation. As chancellor, Bismarck tried without much success to limit the influence of the Roman Catholic Church and of its party-political arm, the Catholic Center Party, in schools and education- and language-related policies. The Catholic Center Party remained particularly well entrenched in the Catholic strongholds of Bavaria and southern Baden, and in urban areas that held high populations of displaced rural workers seeking jobs in the heavy industry, and sought to protect the rights not only of Catholics, but other minorities, including the Poles, and the French minorities in the Alsatian lands.[116] The May Laws of 1873 brought the appointment of priests, and their education, under the control of the state, resulting in the closure of many seminaries, and a shortage of priests. The Congregations Law of 1875 abolished religious orders, ended state subsidies to the Catholic Church, and removed religious protections from the Prussian constitution.[117]
[edit]
In this close-up of the Niederwald Monument (see long shot above), Germania towers 40 meters (131 ft) above the town of Rüdesheim. She holds a crown in her right hand and carries a sword at her side. The Niederwald Germania was erected 1877–1883.
The Germanized Jews remained another vulnerable population in the new German nation-state. Since 1780, after emancipation by the Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II, Jews in the former Habsburg territories had enjoyed considerable economic and legal privileges that their counterparts in other German-speaking territories did not: they could own land, for example, and they did not have to live in a Jewish quarter (also called the Judengasse, or «Jews’ alley»). They could also attend universities and enter the professions. During the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras, many of the previously strong barriers between Jews and Christians broke down. Napoleon had ordered the emancipation of Jews throughout territories under French hegemony. Like their French counterparts, wealthy German Jews sponsored salons; in particular, several Jewish salonnières held important gatherings in Frankfurt and Berlin during which German intellectuals developed their own form of republican intellectualism. Throughout the subsequent decades, beginning almost immediately after the defeat of the French, reaction against the mixing of Jews and Christians limited the intellectual impact of these salons. Beyond the salons, Jews continued a process of Germanization in which they intentionally adopted German modes of dress and speech, working to insert themselves into the emerging 19th-century German public sphere. The religious reform movement among German Jews reflected this effort.[118]
By the years of unification, German Jews played an important role in the intellectual underpinnings of the German professional, intellectual, and social life. The expulsion of Jews from Russia in the 1880s and 1890s complicated integration into the German public sphere. Russian Jews arrived in north German cities in the thousands; considerably less educated and less affluent, their often dismal poverty dismayed many of the Germanized Jews. Many of the problems related to poverty (such as illness, overcrowded housing, unemployment, school absenteeism, refusal to learn German, etc.) emphasized their distinctiveness for not only the Christian Germans, but for the local Jewish populations as well.[119]
Writing the story of the nation[edit]
Another important element in nation-building, the story of the heroic past, fell to such nationalist German historians as the liberal constitutionalist Friedrich Dahlmann (1785–1860), his conservative student Heinrich von Treitschke (1834–1896), and others less conservative, such as Theodor Mommsen (1817–1903) and Heinrich von Sybel (1817–1895), to name two. Dahlmann himself died before unification, but he laid the groundwork for the nationalist histories to come through his histories of the English and French revolutions, by casting these revolutions as fundamental to the construction of a nation, and Dahlmann himself viewed Prussia as the logical agent of unification.[120]
Heinrich von Treitschke’s History of Germany in the Nineteenth Century, published in 1879, has perhaps a misleading title: it privileges the history of Prussia over the history of other German states, and it tells the story of the German-speaking peoples through the guise of Prussia’s destiny to unite all German states under its leadership. The creation of this Borussian myth (Borussia is the Latin name for Prussia) established Prussia as Germany’s savior; it was the destiny of all Germans to be united, this myth maintains, and it was Prussia’s destiny to accomplish this.[121] According to this story, Prussia played the dominant role in bringing the German states together as a nation-state; only Prussia could protect German liberties from being crushed by French or Russian influence. The story continues by drawing on Prussia’s role in saving Germans from the resurgence of Napoleon’s power in 1815, at Waterloo, creating some semblance of economic unity, and uniting Germans under one proud flag after 1871.[122]
Mommsen’s contributions to the Monumenta Germaniae Historica laid the groundwork for additional scholarship on the study of the German nation, expanding the notion of «Germany» to mean other areas beyond Prussia. A liberal professor, historian, and theologian, and generally a titan among late 19th-century scholars, Mommsen served as a delegate to the Prussian House of Representatives from 1863 to 1866 and 1873 to 1879; he also served as a delegate to the Reichstag from 1881 to 1884, for the liberal German Progress Party (Deutsche Fortschrittspartei) and later for the National Liberal Party. He opposed the antisemitic programs of Bismarck’s Kulturkampf and the vitriolic text that Treitschke often employed in the publication of his Studien über die Judenfrage (Studies of the Jewish Question), which encouraged assimilation and Germanization of Jews.[123]
See also[edit]
- Italian unification
- Formation of Romania
- Reichsbürgerbewegung
- Pan-Germanism
- Qin’s wars of Chinese unification
References[edit]
- ^ See, for example, James Allen Vann, The Swabian Kreis: Institutional Growth in the Holy Roman Empire 1648–1715. Vol. LII, Studies Presented to International Commission for the History of Representative and Parliamentary Institutions. Bruxelles, 1975. Mack Walker. German home towns: community, state, and general estate, 1648–1871. Ithaca, 1998.
- ^ John G. Gagliardo, Reich and Nation. The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806, Indiana University Press, 1980, p. 278–279.
- ^ Robert A. Kann. History of the Habsburg Empire: 1526–1918, Los Angeles, 1974, p. 221. In his abdication, Francis released all former estates from their duties and obligations to him, and took upon himself solely the title of Emperor of Austria, which had been established since 1804. Golo Mann, Deutsche Geschichte des 19. und 20. Jahrhunderts, Frankfurt am Main, 2002, p. 70.
- ^ Fichte, Johann Gottlieb (1808). «Address to the German Nation». www.historyman.co.uk. Retrieved June 6, 2009.
- ^ James J. Sheehan, German History, 1780–1866, Oxford, 1989, p. 434.
- ^ Jakob Walter, and Marc Raeff. The diary of a Napoleonic foot soldier. Princeton, N.J., 1996.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 384–387.
- ^ Although the Prussian army had gained its reputation in the Seven Years’ War, its humiliating defeat at Jena and Auerstadt crushed the pride many Prussians felt in their soldiers. During their Russian exile, several officers, including Carl von Clausewitz, contemplated reorganization and new training methods. Sheehan, p. 323.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 322–323.
- ^ David Blackbourn and Geoff Eley. The Peculiarities of German History: Bourgeois Society and Politics in Nineteenth-Century Germany. Oxford & New York, 1984, part 1; Thomas Nipperdey, German History From Napoleon to Bismarck, 1800–1871, New York, Oxford, 1983. Chapter 1.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 398–410; Hamish Scott, The Birth of a Great Power System, 1740–1815, US, 2006, pp. 329–361.
- ^ Lloyd Lee, Politics of Harmony: Civil Service, Liberalism, and Social Reform in Baden, 1800–1850, Cranbury, New Jersey, 1980.
- ^ Adam Zamoyski, Rites of Peace: The Fall of Napoleon and the Congress of Vienna, New York, 2007, pp. 98–115, 239–40.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 398–410.
- ^ Jean Berenger. A History of the Habsburg Empire 1700–1918. C. Simpson, Trans. New York: Longman, 1997, ISBN 0-582-09007-5. pp. 96–97.
- ^ Jonathan Sperber, Rhineland radicals: the democratic movement and the revolution of 1848–1849. Princeton, N.J., 1993.
- ^ L.B. Namier, (1952) Avenues of History. London, ONT, 1952, p. 34.
- ^ Nipperdey, pp. 1–3.
- ^ a b c Sheehan, pp. 407–408, 444.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 460–470. German Historical Institute
- ^ a b Sheehan, pp. 442–445.
- ^ a b Sheehan, pp. 610–613.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 610.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 612.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 613.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 610–615.
- ^ David Blackbourn, Marpingen: Apparitions of the Virgin Mary in Nineteenth-Century Germany. New York, 1994.
- ^ Sperber, Rhineland radicals. p. 3.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, p. 127.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 465–467; Blackbourn, Long Century, pp. 106–107.
- ^ a b Wolfgang Keller and Carol Shiue, The Trade Impact of the Customs Union, Boulder, University of Colorado, 5 March 2013, pp.10 and 18
- ^ Florian Ploeckl. The Zollverein and the Formation of a Customs Union, Discussion Paper no. 84 in the Economic and Social History series, Nuffield College, Oxford, Nuffield College. Retrieved from www.nuff.ox.ac.uk/Economics/History March 2017; p. 23
- ^ Sheehan, p. 465.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 466.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 467–468.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 502.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 469.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 458.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 466–467.
- ^ They traced the roots of the German language, and drew its different lines of development together. The Brothers Grimm online. Joint Publications.
- ^ (in German) Hans Lulfing, Baedecker, Karl, Neue Deutsche Biographie (NDB). Band 1, Duncker & Humblot, Berlin, 1953, p. 516 f.
- ^ (in German) Peter Rühmkorf, Heinz Ludwig Arnold, Das Lied der Deutschen Göttingen: Wallstein, 2001, ISBN 3-89244-463-3, pp. 11–14.
- ^ Raymond Dominick III, The Environmental Movement in Germany, Bloomington, Indiana University, 1992, pp. 3–41.
- ^ (in German) Badische Heimat/Landeskunde online 2006 Veit’s Pauls Church Germania. Retrieved 5 June 2009.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, pp. 138–164.
- ^ Jonathan Sperber, Revolutionary Europe, 1780–1850, New York, 2000.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, pp. 176–179.
- ^ Examples of this argument appear in: Ralf Dahrendorf, German History, (1968), pp. 25–32; (in German) Hans Ulrich Wehler, Das Deutsche Kaiserreich, 1871–1918, Göttingen, 1973, pp. 10–14; Leonard Krieger, The German Idea of Freedom, Chicago, 1957; Raymond Grew, Crises of Political Development in Europe and the United States, Princeton, 1978, pp. 312–345; Jürgen Kocka and Allan Mitchell. Bourgeois Society in Nineteenth-Century Europe. Oxford, 1993; Jürgen Kocka, «German History before Hitler: The Debate about the German Sonderweg.» Journal of Contemporary History, Vol. 23, No. 1 (January, 1988), pp. 3–16; Volker Berghahn, Modern Germany. Society, Economy and Politics in the Twentieth Century. Cambridge, 1982.
- ^ World Encyclopedia V.3 p. 542.
- ^ For a summary of this argument, see David Blackbourn, and Geoff Eley. The Peculiarities of German History: Bourgeois Society and Politics in Nineteenth-Century Germany. Oxford & New York, 1984, part 1.
- ^ Blackbourn and Eley. Peculiarities, Part I.
- ^ Blackbourn and Eley, Peculiarities, Chapter 2.
- ^ Blackbourn and Eley, Peculiarities, pp. 286–293.
- ^ Jürgen Kocka, «Comparison and Beyond.'» History and Theory, Vol. 42, No. 1 (February, 2003), pp. 39–44, and Jürgen Kocka, «Asymmetrical Historical Comparison: The Case of the German Sonderweg«, History and Theory, Vol. 38, No. 1 (February, 1999), pp. 40–50.
- ^ For a representative analysis of this perspective, see Richard J. Evans, Rethinking German History: Nineteenth-Century Germany and the Origins of the Third Reich. London, 1987.
- ^ A. J. P. Taylor, The Struggle for Mastery in Europe 1914–1918, Oxford, 1954, p. 37.
- ^ J.G.Droysen, Modern History Sourcebook: Documents of German Unification, 1848–1871. Retrieved 9 April 2009.
- ^ Zamoyski, pp. 100–115.
- ^ Blackbourn, The Long Nineteenth Century, pp. 160–175.
- ^ The remainder of the letter exhorts the Germans to unification: «This role of world leadership, left vacant as things are today, might well be occupied by the German nation. You Germans, with your grave and philosophic character, might well be the ones who could win the confidence of others and guarantee the future stability of the international community. Let us hope, then, that you can use your energy to overcome your moth-eaten thirty tyrants of the various German states. Let us hope that in the center of Europe you can then make a unified nation out of your fifty millions. All the rest of us would eagerly and joyfully follow you.» Denis Mack Smith (editor). Garibaldi (Great Lives Observed), Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., 1969, p. 76.
- ^ Mack Smith, Denis (1994). Mazzini. Yale University Press. pp. 11–12. ISBN 978-0-300-05884-0.
- ^ Holt, p. 27.
- ^ Holt, pp. 13–14.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, pp. 175–179.
- ^ Hollyday, 1970, pp. 16–18.
- ^ Blackbourn, Peculiarities, Part I.
- ^ Bismarck had «cut his teeth» on German politics, and German politicians, in Frankfurt: a quintessential politician, Bismarck had built his power-base by absorbing and co-opting measures from throughout the political spectrum. He was first and foremost a politician, and in this lied his strength. Furthermore, since he trusted neither Moltke nor Roon, he was reluctant to enter a military enterprise over which he would have no control. Mann, Chapter 6, pp. 316–395.
- ^ Isabel V. Hull, Absolute Destruction: Military culture and the Practices of War in Imperial Germany, Ithaca, New York, 2005, pp. 90–108; 324–333.
- ^ Michael Eliot Howard, The Franco-Prussian War: the German invasion of France, 1870–1871. New York, MacMillan, 1961, p. 40.
- ^ Mann, pp. 390–395.
- ^ A. J. P. Taylor, Bismarck: The Man and the Statesman. Oxford, Clarendon, 1988. Chapter 1, and Conclusion.
- ^ Howard, pp. 40–57.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 900–904; Wawro, pp. 4–32; Holt, p. 75.
- ^ Holt, p. 75.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 900–906.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 906; Geoffrey Wawro, The Austro Prussian War: Austria’s War with Prussia and Italy in 1866. Cambridge, Cambridge University, 1996, pp. 82–84.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 905–906.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 909.
- ^ Wawro, pp. 50–60; 75–79.
- ^ Wawro, pp. 57–75.
- ^ Taylor, Bismarck, pp. 87–88.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 908–909
- ^ The Situation of Germany. (PDF) – The New York Times, July 1, 1866.
- ^ Sheehan, p. 910.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, Chapter V: From Reaction to Unification, pp. 225–269.
- ^ Rosita Rindler Schjerve Diglossia and Power: Language Policies and Practice in the Nineteenth Century Habsburg Empire, 2003, ISBN 3-11-017653-X, pp. 199–200.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 909–910; Wawro, Chapter 11.
- ^ Sheehan, pp. 905–910.
- ^ Bridge and Bullen, The Great Powers and the European States System 1814–1914.
- ^ Howard, pp. 4–60.
- ^ Howard, pp. 50–57.
- ^ Howard, pp. 55–56.
- ^ Howard, pp. 56–57.
- ^ Howard, pp. 55–59.
- ^ Howard, pp. 64–68.
- ^ Howard, pp. 218–222.
- ^ Howard, pp. 222–230.
- ^ G.Wawro. The Franco-Prussian War. The German Conquest of France in 1870–1871. Cambridge University Press.2003. p.235
- ^ Taylor, Bismarck, p. 126
- ^ Howard, pp. 357–370.
- ^ Die Reichsgründung 1871 (The Foundation of the Empire, 1871), Lebendiges virtuelles Museum Online, accessed 2008-12-22. German text translated: […] on the wishes of Wilhelm I, on the 170th anniversary of the elevation of the House of Brandenburg to princely status on January 18, 1701, the assembled German princes and high military officials proclaimed Wilhelm I as German Emperor in the Hall of Mirrors at the Versailles Palace.
- ^ Taylor, Bismarck, p. 133.
- ^ Crankshaw, Edward. Bismarck. New York, The Viking Press, 1981, p. 299.
- ^ Howard, Chapter XI: the Peace, pp. 432–456.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, pp. 255–257.
- ^ G.Wawro. The Franco-Prussian War. The German Conquest of France in 1870–1871. Cambridge University Press.2003. p.302
- ^ Alon Confino. The Nation as a Local Metaphor: Württemberg, Imperial Germany, and National Memory, 1871–1918. Chapel Hill, University of North Carolina Press, 1997.
- ^ Richard J. Evans, Death in Hamburg: Society and Politics in the Cholera Years, 1830–1910. New York, 2005, p. 1.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, p. 267.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, pp. 225–301.
- ^ David Blackbourn and Geoff Eley. The Peculiarities of German History: Bourgeois Society and Politics in Nineteenth-Century Germany. Oxford [Oxfordshire] and New York, Oxford University Press, 1984. Peter Blickle, Heimat: a critical theory of the German idea of homeland, Studies in German literature, linguistics and culture. Columbia, South Carolina, Camden House; Boydell & Brewer, 2004. Robert W. Scribner, Sheilagh C. Ogilvie, Germany: A New Social and Economic History. London and New York, Arnold and St. Martin’s Press, 1996.
- ^ To name only a few of these studies: Geoff Eley, Reshaping the German Right: Radical Nationalism and Political Change After Bismarck. New Haven, 1980. Richard J. Evans, Death in Hamburg: Society and Politics in the Cholera Years, 1830–1910.New York, 2005. Richard J. Evans,Society and politics in Wilhelmine Germany. London and New York, 1978. Thomas Nipperdey, Germany from Napoleon to Bismarck, 1800–1866. Princeton, New Jersey, 1996. Jonathan Sperber, Popular Catholicism in Nineteenth-Century Germany. Princeton, N.J., 1984. (1997).
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, pp. 240–290.
- ^ For more on this idea, see, for example, Joseph R. Llobera, and Goldsmiths’ College. The role of historical memory in (ethno)nation-building, Goldsmiths sociology papers. London, 1996; (in German) Alexandre Escudier, Brigitte Sauzay, and Rudolf von Thadden. Gedenken im Zwiespalt: Konfliktlinien europäischen Erinnerns, Genshagener Gespräche; vol. 4. Göttingen: 2001; Alon Confino. The Nation as a Local Metaphor: Württemberg, Imperial Germany, and National Memory, 1871–1918. Chapel Hill, 1999.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, pp. 243–282.
- ^ Blackbourn, Long Century, pp. 283; 285–300.
- ^ Jonathan Sperber. Popular Catholicism in Nineteenth-Century Germany, Princeton, N.J., 1984.
- ^ Marion Kaplan, The Making of the Jewish Middle Class: Women, Family, and Identity in Imperial Germany, New York, 1991.
- ^ Kaplan, in particular, pp. 4–7 and Conclusion.
- ^ Blackbourn and Eley, Peculiarities, p. 241.
- ^ Karin Friedrich, The other Prussia: royal Prussia, Poland and liberty, 1569–1772, New York, 2000, p. 5.
- ^ Many modern historians describe this myth, without subscribing to it: for example, Rudy Koshar, Germany’s Transient Pasts: Preservation and the National Memory in the Twentieth Century. Chapel Hill, 1998; Hans Kohn. German History: Some New German Views. Boston, 1954; Thomas Nipperdey, Germany History from Napoleon to Bismarck.
- ^ Josep R. Llobera and Goldsmiths’ College. The Role of Historical Memory in (Ethno)Nation-Building. Goldsmiths sociology papers. London, Goldsmiths College, 1996.
Sources[edit]
- Berghahn, Volker. Modern Germany: Society, Economy and Politics in the Twentieth Century. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1982. ISBN 978-0-521-34748-8
- Beringer, Jean. A History of the Habsburg Empire 1700–1918. C. Simpson, Trans. New York: Longman, 1997, ISBN 0-582-09007-5.
- Blackbourn, David, Marpingen: Apparitions of the Virgin Mary in Bismarckian Germany. New York: Knopf, 1994. ISBN 0-679-41843-1
- Blackbourn, David. The Long Nineteenth Century: A History of Germany, 1780–1918. New York: Oxford University Press, 1998. ISBN 0-19-507672-9
- Blackbourn, David and Eley, Geoff. The Peculiarities of German History: Bourgeois Society and Politics in Nineteenth-Century Germany. Oxford & New York: Oxford University Press, 1984. ISBN 978-0-19-873057-6
- Blickle, Peter. Heimat: A Critical Theory of the German Idea of Homeland. Studies in German literature, linguistics and culture. Columbia, South Carolina: Camden House Press, 2004. ISBN 978-0-582-78458-1
- Bridge, Roy and Roger Bullen, The Great Powers and the European States System 1814–1914, 2nd ed. Longman, 2004. ISBN 978-0-582-78458-1
- Confino, Alon. The Nation as a Local Metaphor: Württemberg, Imperial Germany, and National Memory, 1871–1918. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 1997. ISBN 978-0-8078-4665-0
- Crankshaw, Edward. Bismarck. New York, The Viking Press, 1981. ISBN 0-333-34038-8
- Dahrendorf, Ralf. Society and Democracy in Germany (1979)
- Dominick, Raymond, III. The Environmental Movement in Germany, Bloomington, Indiana University, 1992. ISBN 0-253-31819-X
- Evans, Richard J. Death in Hamburg: Society and Politics in the Cholera Years, 1830–1910. New York: Oxford University Press, 2005. ISBN 978-0-14-303636-4
- Evans, Richard J. Rethinking German History: Nineteenth-Century Germany and the Origins of the Third Reich. London, Routledge, 1987. ISBN 978-0-00-302090-8
- Flores, Richard R. Remembering the Alamo: Memory, Modernity, and the Master Symbol. Austin: University of Texas, 2002. ISBN 978-0-292-72540-9
- Friedrich, Karin, The Other Prussia: Royal Prussia, Poland and Liberty, 1569–1772, New York, 2000. ISBN 978-0-521-02775-5
- Grew, Raymond. Crises of Political Development in Europe and the United States. Princeton, Princeton University Press, 1978. ISBN 0-691-07598-0
- Hollyday, F. B. M. Bismarck. New Jersey, Prentice Hall, 1970. ISBN 978-0-13-077362-3
- Holt, Alexander W. The History of Europe from 1862–1914: From the Accession of Bismarck to the Outbreak of the Great War. New York: MacMillan, 1917. OCLC 300969997
- Howard, Michael Eliot. The Franco-Prussian War: The German invasion of France, 1870–1871. New York, MacMillan, 1961. ISBN 978-0-415-02787-8
- Hull, Isabel. Absolute Destruction: Military Culture and the Practices of War in Imperial Germany. Ithaca, New York, Syracuse University Press, 2005. ISBN 978-0-8014-7293-0
- Kann, Robert A. History of the Habsburg Empire: 1526–1918. Los Angeles, University of California Press, 1974 ISBN 978-0-520-04206-3
- Kaplan, Marion. The Making of the Jewish Middle Class: Women, Family, and Identity in Imperial Germany. New York, Oxford University Press, 1991. ISBN 978-0-19-509396-4
- Kocka, Jürgen and Mitchell, Allan. Bourgeois Society in Nineteenth Century Europe. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1993. ISBN 978-0-85496-414-7
- Kocka, Jürgen and Mitchell, Allan. «German History before Hitler: The Debate about the German Sonderweg.» Journal of Contemporary History Vol. 23, No. 1 (January 1988), p. 3–16.
- Kocka, Jürgen and Mitchell, Allan. «Comparison and Beyond.'» History and Theory Vol. 42, No. 1 (February 2003), p. 39–44.
- Kocka, Jürgen and Mitchell, Allan. «Asymmetrical Historical Comparison: The Case of the German Sonderweg«. History and Theory Vol. 38, No. 1 (February 1999), p. 40–50.
- Kohn, Hans. German History; Some New German Views. Boston: Beacon, 1954. OCLC 987529
- Koshar, Rudy. Germany’s Transient Pasts: Preservation and the National Memory in the Twentieth Century. Chapel Hill, 1998. ISBN 978-0-8078-4701-5
- Krieger, Leonard. The German Idea of Freedom, Chicago, University of Chicago Press, 1957. ISBN 978-1-59740-519-5
- Lee, Lloyd. The Politics of Harmony: Civil Service, Liberalism, and Social Reform in Baden, 1800–1850. Cranbury, New Jersey, Associated University Presses, 1980. ISBN 978-0-87413-143-7
- Llobera, Josep R. and Goldsmiths’ College. «The role of historical memory in (ethno)nation-building.» Goldsmiths Sociology Papers. London, Goldsmiths College, 1996. ISBN 978-0-902986-06-0
- Mann, Golo. The History of Germany Since 1789 (1968)
- Namier, L.B. Avenues of History. New York, Macmillan, 1952. OCLC 422057575
- Nipperdey, Thomas. Germany from Napoleon to Bismarck, 1800–1866. Princeton, Princeton University Press, 1996. ISBN 978-0-691-02636-7
- Schjerve, Rosita Rindler, Diglossia and Power: Language Policies and Practice in the Nineteenth Century Habsburg Empire. Berlin, De Gruyter, 2003. ISBN 978-3-11-017654-4
- Schulze, Hagen. The Course of German Nationalism: From Frederick the Great to Bismarck, 1763–1867. Cambridge & New York, Cambridge University Press, 1991. ISBN 978-0-521-37759-1
- Scott, H. M. The Birth of a Great Power System. London & New York, Longman, 2006. ISBN 978-0-582-21717-1
- Scribner, Robert W. and Sheilagh C. Ogilvie. Germany: A New Social and Economic History. London: Arnold Publication, 1996. ISBN 978-0-340-51332-3
- Sheehan, James J. German History 1770–1866. Oxford History of Modern Europe. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1989. ISBN 978-0-19-820432-9
- Sked, Alan. Decline and Fall of the Habsburg Empire 1815–1918. London, Longman, 2001. ISBN 978-0-582-35666-5
- Sorkin, David, The Transformation of German Jewry, 1780–1840, Studies in Jewish history. New York, Wayne State University Press, 1987. ISBN 978-0-8143-2828-6
- Sperber, Jonathan. The European Revolutions, 1848–1851. New Approaches to European History. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1984. ISBN 978-0-521-54779-6
- Sperber, Jonathan. Popular Catholicism in Nineteenth-Century Germany. Princeton, Princeton University Press, 1984. ISBN 978-0-691-05432-2
- Sperber, Jonathan. Rhineland Radicals: The Democratic Movement and the Revolution of 1848–1849. Princeton, Princeton University Press, 1993. ISBN 978-0-691-00866-0
- Stargardt, Nicholas. The German Idea of Militarism: Radical and Socialist Critics, 1866–1914. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1994. ISBN 978-0-521-46692-9
- Steinberg, Jonathan. Bismarck: A Life (2011)
- Taylor, A. J. P., The Struggle for Mastery in Europe 1848–1918, Oxford, Clarendon, 1954. ISBN 978-0-19-881270-8
- Taylor, A. J. P. Bismarck: The Man and the Statesman. Oxford: Clarendon, 1988. ISBN 978-0-394-70387-9
- Victoria and Albert Museum, Dept. of Prints and Drawings, and Susan Lambert. The Franco-Prussian War and the Commune in Caricature, 1870–71. London, 1971. ISBN 0-901486-30-2
- Walker, Mack. German Home Towns: Community, State, and General Estate, 1648–1871. Ithaca, Syracuse University Press, 1998. ISBN 978-0-8014-8508-4
- Wawro, Geoffrey. The Austro-Prussian War. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1996. ISBN 0-521-62951-9
- Wawro, Geoffrey. Warfare and Society in Europe, 1792–1914. 2000. ISBN 978-0-415-21445-2
- Wehler, Hans Ulrich. The German Empire, 1871–1918 (1997)
- Zamoyski, Adam. Rites of Peace: The Fall of Napoleon and the Congress of Vienna. New York, HarperCollins, 2007. ISBN 978-0-06-077519-3
Further reading[edit]
- Bazillion, Richard J. Modernizing Germany: Karl Biedermann’s career in the kingdom of Saxony, 1835–1901. American university studies. Series IX, History, vol. 84. New York, Peter Lang, 1990. ISBN 0-8204-1185-X
- Brose, Eric Dorn. German History, 1789–1871: From the Holy Roman Empire to the Bismarckian Reich. (1997) online edition
- Bucholz, Arden. Moltke, Schlieffen, and Prussian War Planning. New York, Berg Pub Ltd, 1991. ISBN 0-85496-653-6
- Bucholz, Arden. Moltke and the German Wars 1864–1871. New York, Palgrave MacMillan, 2001. ISBN 0-333-68758-2
- Clark, Christopher. Iron Kingdom: The Rise and Downfall of Prussia, 1600–1947. Cambridge, Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 2006, 2009. ISBN 978-0-674-03196-8
- Clemente, Steven E. For King and Kaiser!: The Making of the Prussian Army Officer, 1860–1914. Contributions in military studies, no. 123. New York: Greenwood, 1992. ISBN 0-313-28004-5
- Cocks, Geoffrey and Konrad Hugo Jarausch. German Professions, 1800–1950. New York, Oxford University Press, 1990. ISBN 0-19-505596-9
- Droysen, J.G. Modern History Sourcebook: Documents of German Unification, 1848–1871. Accessed April 9, 2009.
- Dwyer, Philip G. Modern Prussian history, 1830–1947. Harlow, England, New York: Longman, 2001. ISBN 0-582-29270-0
- Friedrich, Otto. Blood and Iron: From Bismarck to Hitler the Von Moltke Family’s Impact On German History. New York, Harper, 1995. ISBN 0-06-016866-8
- Groh, John E. Nineteenth-Century German Protestantism: The Church As Social Model. Washington, D.C., University Press of America, 1982. ISBN 0-8191-2078-2
- Henne, Helmut, and Georg Objartel. German Student Jargon in the Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries. Berlin & NY, de Gruyter, 1983. OCLC 9193308
- Hughes, Michael. Nationalism and Society: Germany, 1800–1945. London & New York, Edward Arnold, 1988. ISBN 0-7131-6522-7
- Kollander, Patricia. Frederick III: Germany’s Liberal Emperor, Contributions to the study of world history, no. 50. Westport, Conn., Greenwood, 1995. ISBN 0-313-29483-6
- Koshar, Rudy. Germany’s Transient Pasts: Preservation and the National Memory in the Twentieth Century. Chapel Hill, University of North Carolina Press, 1998. ISBN 0-8078-4701-1
- Lowenstein, Steven M. The Berlin Jewish Community: Enlightenment, Family, and Crisis, 1770–1830. Studies in Jewish history. New York, Oxford University Press, 1994. ISBN 0-19-508326-1
- Lüdtke, Alf. Police and State in Prussia, 1815–1850. Cambridge, New York & Paris, Cambridge University Press, 1989. ISBN 0-521-11187-0
- Ogilvie, Sheilagh, and Richard Overy. Germany: A New Social and Economic History Volume 3: Since 1800 (2004)
- Ohles, Frederik. Germany’s Rude Awakening: Censorship in the Land of the Brothers Grimm. Kent, Ohio, Ohio State University Press, 1992. ISBN 0-87338-460-1
- Pflanze Otto, ed. The Unification of Germany, 1848–1871 (1979), essays by historians
- Schleunes, Karl A. Schooling and Society: The Politics of Education in Prussia and Bavaria, 1750–1900. Oxford & New York, Oxford University Press, 1989. ISBN 0-85496-267-0
- Showalter, Dennis E. The Wars of German Unification (2nd ed. 2015), 412pp by a leading military historian
- Showalter, Dennis E. Railroads and Rifles: Soldiers, Technology, and the Unification of Germany. Hamden, Connecticut, Hailer Publishing, 1975. ISBN 0-9798500-9-6
- Smith, Woodruff D. Politics and the Sciences of Culture in Germany, 1840–1920. New York, Oxford University Press, 1991. ISBN 0-19-506536-0
- Wawro, Geoffrey. The Franco-Prussian War: The German Conquest of France. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2005. ISBN 0-521-61743-X
External links[edit]
- Documents of German Unification
- Bismarck and the Unification of Germany
План урока:
Образование Германского союза
Германская революция
Экономика Германии в 40-60-х гг.
Образование Северогерманского союза
Объединение Германии в единую империю
Экономическое развитие Германии после объединения
Милитаризация Германии
Образование и развитие Германского союза
После поражения Наполеона в 1815 году Венским конгрессом было принято решение об образовании Германского союза – конфедерации[1], состоявшей из 35 самостоятельных государств и 4 независимых городов. Эти территории обладали суверенитетом, в каждом из государств была своя монархическая династия, свое правительство, законы, армия, валюта. В одних государствах сохранялось самодержавие, в других были приняты конституции, и реальная власть принадлежала парламенту.
Запоминаем новые слова!
Суверенитет – независимость государства в ведении внутренней и внешней политики.
Во главе Германского союза стоял Союзный сейм, но этот представительный орган не обладал реальной властью, его решения не были обязательны для отдельных членов Германского союза. Ведущую роль в Германском союзе играли самые большие и экономически развитые Австрия и Пруссия, которые в будущем стали бороться за роль лидера в объединении Германии.
Из-за политической раздробленности в начале 19 века Германия сильно отставала в своем экономическом развитии от Англии, Франции и других европейских держав. Таможенные границы между 35 монархиями сдерживали развитие торговли и промышленности (из-за затруднений с перевозкой сырья и готовой продукции). Политическая раздробленность Германии была выгодна ее соседям, избавившимся таким образом от конкурента в международной торговле.
В 1834 году по предложению Пруссии был создан Немецкий таможенный союз. В него вошли 18 государств, уничтожившие внутренние таможенные границы Германского союза, для свободной транспортировки сырья и продукции на собственных территориях. Оставшиеся монархии сохранили таможенные границы, что создавало препятствия для развития германской торговли и промышленности.
Германская революция 1848-1849гг.
Французская революция 1848 года спровоцировала революционный подъем во многих европейских государствах, в том числе и в Германии. Однако в раздробленной Германии революции происходили в разных монархиях в разное время, революционеры не сумели объединить свои силы. Германские повстанцы требовали:
- принятия конституции в Германии;
- предоставления гражданам прав и свобод – равенства всех перед законом, свободы слова, совести, собраний;
- созыва общегерманского парламента;
- введения всеобщего избирательного права;
- объединения Германии.
В начале марта революционные волнения охватили Баварию, Саксонию, Вюртемберг, Гессен-Дармштадт. 18 марта началось восстание в Берлине — столице Пруссии. 18 мая 1848 года состоялось первое заседание общегерманского парламента – Национального собрания, которое представляли более 400 депутатов из различных германских княжеств.
Парламент провозгласил равенство всех перед законом, отменил сословные привилегии, принял новую общегерманскую конституцию. Главой объединенной империи парламент предложил стать прусскому королю – Фридриху Вильгельму IV. Однако первые революционные преобразования были отменены, так как большинство германских монархов отказалось принимать новую конституцию.
Основная задача революционеров — объединение Германии так и не была решена, поражение в революции отложило этот вопрос более чем на два десятилетия.
Экономика Германии в 40-60-е гг.
В 40-50 годы германские государства стали на путь индустриализации. Активно строились фабрики, железные дороги, развивалась торговля. Десятки тысяч разорившихся крестьян уходили в города, пополняя ряды наемных рабочих. На территориях Германского союза в полную силу развернулся промышленный переворот.
Центрами промышленного производства стали Саксония, Берлин, Рейнская область, Силезия. Здесь занимались добычей угля, выплавкой металлов, производством ситца, машиностроением. Промышленность Германии развивалась благодаря внедрению машин на производство, заимствованию технических изобретений со всего мира, нещадной эксплуатации немецких наемных рабочих.
Образование Северогерманского союза
Новый этап борьбы за объединение Германии был связан с противостоянием Австрии и Пруссии, каждое из этих государств претендовало на роль лидера в создании Германской империи. Из всех союзных государств Австрия господствовала на самом обширном пространстве земель. Лидирующую роль Пруссии в Германском союзе обеспечивала ее промышленная мощь, удачное пересечение торговых путей.
Важную роль в объединении Германии сыграл канцлер (глава германского правительства) Отто фон Бисмарк. Политика Бисмарка предусматривала только один путь к объединению страны- войну Пруссии с другими союзными монархиями и захват территорий.«Не речами и постановлениями, а железом и кровью решаются великие вопросы современности» — говорил Отто фон Бисмарк.
Это интересно!
Отто фон Бисмарк — германский государственный деятель, прозванный «Железным канцлером», живший с 1815 по 1898 годы. Свою славу Бисмарк заслужил будучи дипломатом, а в 1862 году он был назначен на должность канцлера — председателя правительства. Отто фон Бисмарк оставался главой правительства в течение долгих 19 лет, при нем на престоле сменились три Прусских монарха — Вильгельм I, Фридрих II и Вильгельм II. Канцлер Отто Бисмарк превратил Пруссию в доминирующую силу в Германском союзе, оказывал сильное влияние на политику Германской империи плоть до своей отставки в 1890 году.
Первым шагом в политике Отто фон Бисмарка стала война против Дании, которую развязала Пруссия в 1864 году. Союзником Пруссии стала Австрия, которая после разгрома Дании, разделила с Пруссией захваченные территории — Шлезвиг и Гольштейн. В 1866 году Пруссия вторглась на территории Австрии, вынудила ее выйти из Германского союза и отказаться от Шлезвига и Гольштейна. В тоже время Пруссия захватила северогерманские государства — Гессен-Кастель, Франкфурт, Ганновер, Нассау.
В результате устранения Австрии Пруссия стала единственным инициатором объединения Германии. Под ее руководством в августе 1866 года из 22 германских монархий был образован Северогерманский союз. Находящийся в центре Германии, Северогерманский союз учредил свою конституцию, собственный парламент и Союзный совет для управления новым национальным государством. Главой Северогерманского союза был назначен президент — прусский король Вильгельм I. С оставшимися монархиями, союз подписал военные и таможенные договоры.
Объединение Германии в единую империю
Императора Франции Наполеона III сильно встревожили вести об образовании Северогерманского союза. Он обеспокоился растущей мощью Германии, которая все ближе продвигалась к границам французского государства.
19 июля 1870 года Франция объявила войну Пруссии. Однако Франция сильно переоценила свои возможности. Уже в январе 1871 года Прусский император подписывал договор о капитуляции Парижа, Франция сдалась на волю победителя. Франция передала Северогерманскому союзу Эльзас и Лотарингию. 18 января 1871 года прусский король Вильгельм I находясь в Версальском дворце, провозгласил себя императором, а Германия стала единой империей.
В государстве была создана единая почтовая система, введена общенациональная валюта — золотая марка, учреждено единое законодательство и образована единая армия, насчитывавшая более 400 тысяч военнослужащих.
Наряду с императором, управление новым государством было поручено имперскому парламенту. Он состоял из верхней палаты — Бундесрата, депутаты которой назначались правительствами государств, входящих в состав Германской империи. Депутатов нижней палаты – Рейхстага — избирало мужское население, достигшее двадцатипятилетнего возраста.
Превосходство Бундесрата над Рейхстагом было очевидно, верхняя палата могла издавать законы без согласия нижней палаты и даже наперекор ей. Председателем верхней палаты назначался прусский канцлер, поэтому за Пруссией оставалось последнее слово в принятии любого закона или постановления.
Экономическое развитие Германской империи
В 70-90-е годы германская экономика переживает невиданный подъем, благодаря которому бывшая еще недавно отсталым аграрным государством Германская империя превратилась в мощную индустриальную державу.
Основные причины подъема экономики Германии в 70-90-е годы:
- Разграбление Германией Французского государства. После франко-прусской войны Германская империя отобрала у Франции Эльзас и Лотарингию, богатые цветными металлами и каменным углем. Кроме того, положительно сказались на развитии промышленности Германии послевоенные выплаты побежденной Франции – 5 миллиардов франков.
- Складывание внутригосударственного рынка в результате объединения Германии в единую империю в 1871 году.
- Внедрение на производство передовых достижений науки и техники, разработанных как иностранными учеными, так и немецкими (благодаря новой системе образования немецкая наука уже не уступала в своем развитии английской, французской и американской).
- Демографический взрыв — рост численности населения на 2/3 за 70-90-е гг.
- Появление новых отраслей экономики- химической и электротехнической.
В результате развития торговли, промышленности и банковского дела, в Германской империи в 90-е годы сформировался монополистический капитализм.
Запоминаем новые слова!
Монополистический капитализм — это высшая стадия развития капитализма, при которой огромные концентрации капитала приводят к созданию монополий. Монополии играют решающую роль в хозяйственной жизни страны, вступают в международные монополистические союзы. Господствующие монополии устанавливают контроль над мелкими и средними производителями, обретают власть не только в экономической жизни общества, но и в политике.
Обогащение монополий происходило за счет усиления эксплуатации рабочего класса, вывоза товаров и капиталов Германии за границу. В 90-е годы монополии контролировали все электротехническое производство, добычу угля, химическую промышленность, производство стали, железнодорожную отрасль.
Милитаризация Германии
Германская модель экономики шла по пути милитаризации – увеличения военного сектора в государстве. Большая часть предприятий тяжелой промышленности выполняла военные заказы, которые поступали от немецкого правительства, готовящегося к предстоящей войне.
Среди германского населения распространялись идеи национализма и шовинизма – идея исключительности германской нации, приоритета национальных интересов германского народа, непримиримой вражды между Германской империей и соседними государствами.
Словарь
1. Конфедерация – союзное объединение самостоятельных государств.
Провозглашение Германской империи в Версальском дворце под Парижем в 1871 г. Картина А. Вернера
150 лет назад создан Второй рейх. 18 января 1871 года монархи всех германских государств в торжественной обстановке в Версале провозгласили прусского короля Вильгельма германским императором. Германия была объединена «железом и кровью» канцлером Отто фон Бисмарком и Вильгельмом.
Пруссия в ходе Франко-прусской войны 1870–1871 гг. сокрушила главного противника на континенте – Францию. Германия была создана в ходе войны, но в целом для германского народа это было прогрессивное явление.
Необходимость объединения Германии
Ещё во времена войн Наполеона под влиянием Французской революции возник германский национализм и пангерманизм. Немецкие националисты считали, что современные германцы наследники древнего германского этноса, но живут в разных государствах.
Раздробленность Германии отрицательно сказывается на народе, экономике и военно-политической мощи. Сформировалось пангерманское культурное и политические движение.
С другой стороны, в XIX веке быстро развивалась экономика, росла численность буржуазии, городского «среднего класса». В интеллигенции, студенчестве распространялись либеральные идеи. Объединение Германии было прогрессивным шагом, нужно было разрушить старые границы, различные законы, таможни, денежные единицы, феодальные порядки (цеховая организация и пр.), привести всё к единообразию. Создать единое правительство, конституцию, систему управления, денежную единицу, экономику, армию и т.д.
При этом на Венском конгрессе, после разгрома империи Наполеона, раздробленность Германии была сохранена. В 1814 году создан Германский союз из 38 государств. Это была конфедерация независимых государств.
Высшим органом Союза был бундестаг (Союзный сейм), члены которого назначались монархами. Заседания Союза проводились во Франкфурте-на-Майне. Главой Союза формально считался император Австрии.
Каждое государство Союза сохраняло суверенитет, в одном – король имел абсолютную власть, в других – имелись сословно-представительные собрания, в нескольких –
конституции. Империя Габсбургов долгое время занимала доминирующие позиции в Германии. Однако Вена в силу различных причин не могла объединить Германию. Поэтому австрийцы всеми силами старались помешать главному конкуренту – Пруссии.
Великогерманский и малогерманский пути
В Германии было две ведущих идеи по созданию единого государства.
Великогерманский путь предполагал объединение страны во главе с австрийским императором. Проблема была в том, что Австрийская империя была многонациональным государством. И немцы там не были большинством (более половины населения – славяне, также крупным народом были венгры). Кроме того, дом Габсбургов проводил более консервативную политику, чем многие другие германские монархии. Это был оплот абсолютизма и старых порядков. Поэтому поддержка у этого плана в германском обществе была минимальной. По мере роста проблем у Австрии (с 1867 года – Австро-Венгрия) поддержка этой программы стала минимальной.
Наоборот, малогерманский путь – объединение вокруг Прусского королевства без участия Австрии, стал более привлекательным для немцев.
Европейские революции 1848–1849 гг. привели к активизации либерально-демократических и национальных настроений в Германии. Во многих германских землях к власти пришли более либеральные правительства. Австрийская империя из-за венгерского восстания оказалась под угрозой развала. В Германских землях националисты поставили вопрос о преобразовании Союза в федерацию.
Бундестаг в мае 1848 года заменили на Франкфуртское национальное собрание (первый общегерманский парламент). Началась дискуссия об общегерманской конституции. Попытка создать единое правительство провалилась. Пока либералы занимались болтовнёй о будущем страны, консервативные силы перешли в контрнаступление. Первые успехи революции были ликвидированы во многих германских государствах.
В итоге в 1849 году парламент предложил императорскую корону прусскому королю Фридриху-Вильгельму IV (малогерманский путь), но тот отказался принять её от «беспризорников». Пруссия отказала парламенту в легитимности, отозвала своих представителей и силой подавила революцию. Парламент в конце мая 1849 года разогнали.
Революция показала, что объединение неизбежно. Прусская верхушка решила, что нужно провести процесс «сверху», пока он не пошёл «снизу». Также стало ясно, что Австрийская империя, которая устояла только с помощью России, не сможет возглавить процесс объединения Германии. Империя Габсбургов была «лоскутной империей», и входившие в её состав народы, особенно венгры, не желали усиления немецкого элемента в стране. А «восточные немцы» были не готовы отделиться от территорий, не населённых немцами.
Германский союз перед началом Австро-прусской войны 1866 год
«Железом и кровью»
Пруссия, воспользовавшись ослаблением Австрии и видя в обществе соответствующую поддержку, возглавила процесс объединения Германии. В 1849 году был создан Прусский союз (Союз трёх королей), в котором Саксония и Ганновер отдали Берлину внешнюю политику и военную сферу.
К этому союзу примкнули 29 государств. Австрия вынуждена была заключить с Пруссией соглашение о совместном управлении Германией. В 1850 году была восстановлена деятельность Германского союза (созван Франкфуртский сейм). Пруссия сначала противилась этому, но под давлением России и Австрии уступила.
Новый этап в деле объединения Германии связан с именем Отто фон Бисмарка («Железный канцлер» Отто фон Бисмарк; Часть 2; Часть 3). Он в 1862 году возглавил прусское правительство. По мнению Бисмарка, главную роль в объединении играла военная мощь Пруссии:
«Не высокопарными речами и голосованием большинства, но железом и кровью решаются великие вопросы современности»
(в сущности, такую же политику ранее проводил и Наполеон).
Бисмарк был выдающимся государственным деятелем и смог осуществить свою программу военно-экономического, политического усиления Пруссии (ядра Германии) и объединения страны.
Первыми шагами в объединении Германии стала война с Данией и Австрией.
В 1864 году Пруссия и Австрия разбили Данию, решив вопрос Шлезвига и Гольштейна. Дания по Венскому миру уступила права на герцогства Шлезвиг, Гольштейн и Лауэнбург императору Францу-Иосифу и королю Вильгельму.
В 1866 году прусская армия стремительно разгромила австрийцев. По Пражскому мирному договору Вена передавала Берлину Гольштейн и выходила из Германского союза. Пруссия аннексировала Ганновер, Гессен-Кассель, Гессен-Хомбург, Франкфурт-на-Майне и Нассау.
Вместо Германского союза создан Северогерманский союз во главе с Пруссией. Пруссия стала контролировать войска союзных государств. Южногерманские государства (королевства Бавария и Вюртемберг, герцогство Баден, ландграфство Гессен-Дармштадт) не вошли в Северогерманский союз, однако заключили с Берлином военный союз.
Прусское королевство теперь не имело конкурентов в германском мире. Австрия переживала новую волну кризиса.
Россия соблюдала нейтралитет и этим помогла Пруссии. Фактически Петербург отомстил Австрии за её враждебную позицию во время Крымской войны, во многом из-за которой война и была проиграна. В дальнейшем Россия позволила разгромить и Францию, что позволило частично отменить унизительные статьи Парижского мира 1856 г.
Интересы германской буржуазии были поддержаны введением свободы передвижения внутри Германии, единой системы мер и весов, разрушением цеховых ограничений, развитием промышленности и транспорта. Сложился союз буржуазии и правительства. Средний класс был кровно заинтересован в завершении объединения страны и дальнейшей экспансии.
Главным противником объединения Германии во главе с Пруссией стала Франция. Император Наполеон III считал себя полноценным преемником великодержавной политики Наполеона. Франция должна была господствовать в Западной Европе и помешать объединению Германии. При этом французы были уверены в победе своей армии, считали её сильнее прусской (противника сильно недооценили, свои силы переоценили).
Французское правительство дало себя спровоцировать, чтобы
«наказать пруссаков».
Однако Пруссия, в отличие от Франции, к войне готовилась. Её армия была лучше подготовлена морально и материально. Французы потерпели сокрушительное и позорное поражение в войне 1870–1871 гг. Французские армии были разбиты, окружены и пленены, стратегические крепости сдались. Попал в плен и сам французский император. В Париже началась революция, которая свергла режим Наполеона III и установила Третью республику. Прусские войска осадили Париж.
Германская империя
Южногерманские государства вошли в состав Северогерманского союза.
10 декабря 1870 года рейхстаг союза по предложению канцлера Бисмарка преобразовал Северогерманский союз в Германскую империю, конституцию союза – в конституцию Германии, а пост президента – в пост германского императора.
18 января 1871 года прусский король Вильгельм во дворце французских монархов Версале был провозглашён императором. 16 апреля принята имперская конституция. В союз вошли 22 государства и 3 «вольных» города (Гамбург, Бремен, Любек). Государства сохранили некоторую самостоятельность – свои правительства и собрания (ландтаг). Сохранялись местные дистанции, чтобы укрепить монархический дух и традиции.
Во главе империи были император (он же прусский король), канцлер, Союзный совет (58 членов) и рейхстаг (397 депутатов). Император обладал огромной властью: верховный главнокомандующий, назначал и смещал имперского канцлера, единственного общеимперского министра. Канцлер нёс ответственность только перед кайзером и мог не считаться с мнением рейхстага.
Рейхстаг обсуждал проекты новых законов и принимал бюджет. Принятый рейхстагом законопроект мог стать законом только при утверждении Союзным советом и кайзером. Союзный совет состоял из людей, которые назначались правительствами бывших немецких государств, и представлял их. Рейхстаг избирали на основе всеобщего избирательного права. Женщины, мужчины моложе 25 лет и военные были лишены права голоса.
Пруссия сохранила доминирующие позиции в империи: 55 % территории, свыше 60 % населения, прусская элита преобладала в вооруженных силах, в высшей бюрократии.
Французское правительство, опасаясь радикальных революционеров, предпочло 10 мая 1871 года во Франкфурте-на-Майне заключить с Германией
«похабный мир».
В состав империи вошла новая провинция – Эльзас и Лотарингия. Франция выплачивала большую контрибуцию, которая была направлена на развитие страны.
Победа над Францией стала политической и экономической основой Второго рейха.
Прусский триумвират 1860-х годов, превративший Германию во второй половине XIX века в великую державу. Слева направо: «железный канцлер» Отто фон Бисмарк; военный министр Пруссии, реформатор армии и его ближайший соратник Альбрехт фон Роон; видный деятель военной науки, начальник Генштаба Хельмут фон Мольтке.
Священная Римская империя, создание которой относят к 962 году, объединила огромные территории. В период расцвета в неё входили земли современных Нидерландов, Италии, Чехии и Германии. Однако со временем централизация власти ослабевала, после 18-го века империя стала одним из самых рыхлых государственных формирований Европы.
На фоне масштабных проблем внутри империи среди огромного количества мелких германских княжеств на лидирующие роли вышли эрцгерцогство Австрия и королевство Пруссия. В 18-м веке усиливалась австрийская экспансия по южному и восточному направлениям, в то же время Пруссия доминировала на германских землях.
Большой переполох на политической карте Европы устроил Наполеон: его военные походы, по большому счёту, и прекратили существование Священной Римской империи. После поражения Австрии было решено кардинальным образом изменить структуру государства: после преобразования она стала объединять фактически независимые страны. 6 августа 1806 года император Франц II сложил с себя все полномочия, Священная Римская империя официально прекратила своё существование.
Франкфуртский парламент. (wikipedia.org)
1830-е годы стали временем, когда германские княжества под влиянием индустриализации стремились к наращиванию экономической силы. Для этих целей крупнейшие земли в 1834 году объединились в Германский таможенный союз. Внутри союза отсутствовали таможенные барьеры, а на товары из других стран был введён единый тариф.
Вдохновлённые идеей единой Германии в 1848 году немцы вышли на улицы крупных городов, требуя создания централизованного государства. Во Франкфурте-на-Майне появилось даже революционное национальное Всегерманское собрание. Однако Пруссия, Бавария, Австрия и Саксония не поддержали выдвинутых инициатив, и вспыхнувшие волнения были подавлены прусскими войсками.
Бисмарк манипулирует Россией, Австрией и Германией. (wikipedia.org)
Как и раньше, Пруссия и Австрия оставались главными игроками в гонке за объединение Германии под своим началом. Отто фон Бисмарк, на тот момент обычный прусский чиновник высокого ранга, постепенно укреплял свои позиции в правящих кругах. Его главной целью было во что бы то ни стало, используя самые разные методы, объединить Германию.
«Германия слишком тесна для Австрии и Пруссии», — говорил политик в преддверии большой Австро-прусской войны. В 1866 году, занимая пост министра иностранных дел, Бисмарк решился на рискованный шаг — будущий «железный канцлер» пошёл на открытый вооруженный конфликт с Австрией. «Если нас разобьют, я не вернусь сюда. Я погибну в последней атаке. Умереть можно лишь однажды, и побеждённому лучше всего умереть», — сказал он тогда.
Летом 1866 года Бисмарк обратился к народу Германии с проникновенной речью. Искушённый дипломат и умелый политик, он представил Пруссию жертвой австрийской агрессии, выставил дело так, что, казалось, Австрия развязывает этот конфликт. В войну по заключённому втайне договору вступила Италия, также к прусским войскам присоединились небольшие армии северогерманских княжеств.
Итальянская армия не смогла долго бороться с превышавшей по силе австрийской армией, однако главную свою задачу она, безусловно, выполнила. Австрийские главнокомандующие вынуждены были вести войну на два фронта. В то же время пруссаки победоносным маршем шли по баварским землям, встречая только неукомплектованные, не успевшие полностью мобилизоваться части южногерманской армии. К середине июля прусская армия была на подступах к Вене. Продолжение войны могло привести к развалу Австрийской империи, поскольку, чувствуя слабость государства, в Венгрии стали подниматься местные сепаратисты. Бисмарк поспешил с заключением мирного договора: война закончилась быстрее, чем великие державы успели опомниться. По итогам войны Австрия вышла из Германского союза.
На захваченных территориях прусские власти давили на местных монархов, чтобы те не пытались бороться за реставрацию собственной власти. Спустя буквально несколько недель после окончания войны Бисмарк разработал документ, в рамках которого государства Северной Германии заключали с Пруссией союз, а в дальнейшем должны были интегрироваться. Главой Северогерманского союза стал прусский король.
Провозглашение Германской империи в Версальском дворце. (wikipedia.org)
Идея объединения Германии вспыхнула с новой силой, когда раздались очередные залпы ружей. В войне Пруссии и Франции 1870 года южногерманские государства сразу же заняли позицию пруссаков и Северогерманского союза. Абсолютно не подготовленная к войне французская армия терпела одно поражение за другим, чем обеспечивала колоссальный подъём национального самосознания среди немцев.
28 января 1871 года Париж капитулировал, а южногерманские государства начали переговоры с Северогерманским союзом о присоединении. 10 декабря 1870 года Отто фон Бисмарк буквально принёс прусскому королю Вильгельму I императорскую корону. Так начал своё существование Deutsche Reich, или Германская империя.
| Объединение Германии | |
 |
|
| Момент времени | 18 января 1871 |
|---|---|
Объединение Германии вокруг Пруссии в 1807—1871
Объединение Германии (1871) — создание в 1871 году вокруг королевства Пруссия федеративного государства Германская империя из нескольких десятков независимых государств с немецким населением.
Объединение Германии традиционно рассматривают как политический процесс на протяжении 1864—1870 годов, в ходе которого Пруссия провела ряд военных кампаний против Дании, Австрии и Франции. Датой объединения Германии считается 18 января 1871 года, когда после провозглашения Германской империи прусский король Вильгельм I принял присягу в качестве германского императора.
Содержание
- 1 Предыстория объединения
- 1.1 История германской государственности
- 1.2 Герцогство Австрия
- 1.3 Королевство Пруссия
- 1.4 Эпоха наполеоновских войн
- 2 Предпосылки объединения
- 2.1 Общественно-политическая ситуация в Европе
- 2.2 Стремление немцев к объединению. Революция 1848 года.
- 2.3 Прусский союз. Попытка объединения в 1849 году
- 2.4 Внешнеполитическая обстановка для Пруссии в 1860-х
- 2.5 Внутриполитическая обстановка в Пруссии в 1860-х
- 3 Датско-прусская война 1864 года
- 3.1 Причины датско-германского конфликта
- 3.2 Начало датско-германской войны
- 3.3 Победа австро-прусской коалиции
- 4 Австро-прусская война 1866 года
- 4.1 Подготовка австро-прусской войны
- 4.2 Дипломатическая активность Бисмарка
- 4.3 Ход боевых действий
- 4.4 Результат австро-прусской войны
- 5 Северогерманский союз. 1867—1870 годы
- 5.1 Образование Северогерманского союза
- 5.2 Южногерманские государства
- 5.3 Политическая ситуация в Германии в 1870 году
- 6 Франко-прусская война 1870—71 годов
- 6.1 Франко-прусская война
- 6.2 Внешнеполитическая ситуация для Франции и Пруссии
- 6.3 Ход боевых и дипломатических действий
- 7 Объединённая Германия
- 7.1 Объединение германских государств
- 7.2 Германская империя
- 8 Примечания
- 9 Ссылки и источники
Предыстория объединения
История германской государственности
В эпоху Великого переселения народов мигрирующие германские племена с севера Европы разошлись по всем концам континента, создав варварские государства от державы готов в Северном Причерноморье до королевства вандалов в Северной Африке. В новых завоёванных местностях пришлые племена смешивались с местными, более многочисленными и часто более цивилизованными народами, в результате чего потеряли национальную идентичность. Часть территорий, оставленных в первых веках нашей эры германцами, заселили западные славяне. К IX веку близкие по языку германские народы занимали территорию от Рейна до Эльбы, от Балтики до Италии.
Создание первых государств в Европе после падения Римской империи шло не по национальному признаку, а путём военных походов и подчинения мечом соседних племён. Вассалитет преобладал над национальным самосознанием, религиозные убеждения значили больше национальности. В начале IX века большая часть Западной Европы была объединена в державе Карла Великого, тогда же феодальные отношения начали оформлять общественно-политический племенной уклад германцев в сложную иерархическую структуру, объединявшей сотни территориально-государственных образований на землях Германии. Раздел франкской империи Карла Великого привел к образованию Восточнофранкского королевства, примерно совпадавшего в границах с современной Германией. Как пишет Ксантенский анналист под 869 годом, первый его король, Людовик Немецкий, правил «у славян, в Баварии, Алемании и Реции, Саксонии, Швабии, Тюрингии и Франконии с областями Вормсфельд и Шпейер».
Восточнофранкский король Оттон I значительно расширил границы королевства, преобразовав его в 962 году в «Священную Римскую империю германской нации», куда впоследствии были включены славяне, итальянцы, швейцарцы, венгры и другие народы. Священная Римская империя стала весьма рыхлым децентрализованным государственным образованием, в котором существовало два уровня власти: формальный имперский и удельный территориальный, часто конфликтовавших между собой.
После пресечения династии Гогенштауфенов в 1250 году в Священной Римской империи начался длительный период междуцарствия (1254—1273). Но и после его преодоления и вступления на престол в 1273 году Рудольфа I Габсбурга значение центральной власти продолжало падать, а роль правителей региональных княжеств — возрастать. Хотя монархи и предпринимали попытки восстановить былое могущество империи, на первый план вышли династические интересы: удельные правители прежде всего старались максимально расширить владения своих семей: Габсбурги закрепились в австрийских землях, Люксембурги — в Чехии, Моравии и Силезии, Виттельсбахи — в Бранденбурге, Голландии и Геннегау. Именно в позднее средневековье принцип выборности императора приобрел реальное воплощение: на протяжении второй половины XIII — конца XV века император действительно выбирался из нескольких кандидатов, а попытки передачи власти по наследству обычно не имели успеха. Резко возросло влияние крупных территориальных князей на политику империи, причём семь наиболее могущественных князей-курфюрстов присвоили себе исключительное право избрания и смещения императора.
В XVII веке, когда в Европе давно сформировались сильные национальные монархии, Священную империю раздирали внутренние политические, религиозные и национальные противоречия. Вестфальский мир 1648 года после Тридцатилетней войны закрепил политическую раздробленность империи (более 300 субъектов), однако вместе с тем позволил сгладить ряд противоречий и обеспечил мирное развитие германских государств внутри империи.
К середине XVIII века среди множества мелких германских княжеств и удельных владений выделились два крупных, политически единых государства: королевство Пруссия и эрцгерцогство Австрия, родовое владение правящей императорской династии Габсбургов.
Герцогство Австрия
На территории Австрии в позднюю античность жили романизированные кельты. В эпоху переселения народов туда мигрировали германские племена ругиев, лангобардов, баваров, позднее славяне.
Пограничные со славянами и венграми германские земли были преобразованы императором Священной империи Фридрихом Барбароссой в 1156 году в Австрийское герцогство. В 70-х годах XIII века Австрия перешла в наследственное владение дома Габсбургов, которые с 1438 года стали правящей династией Священной Римской империи. В отличие от других княжеств империи Австрийское герцогство расширялось за счёт не германских народов, главным образом славян, итальянцев и венгров. Экспансия Австрии в южном и восточном направлениях отвлекала внимание и силы Габсбургов от общегерманских дел, где с середины XVIII века на первые роли выдвинулась военно-феодальная Пруссия.
Королевство Пруссия
Ядром Пруссии стало маркграфство Бранденбург, которое образовалось в XII веке на славянских землях бодричей и лютичей между Эльбой и Одером в результате экспансии немецких рыцарей на восток. В 1415 году бранденбургские земли стали наследственным владением семьи Гогенцоллернов, выходцев из Баварии, в качестве награды за их поддержку правящей династии «Священной Римской империи».
В 1618 году в результате династического брака сына маркграфа Бранденбурга и дочери герцога Пруссии (из другой ветви Гогенцоллернов) образовалось наследственное владение Бранденбург-Пруссия. Герцогство Пруссия располагалось на землях балтийских племён пруссов, захваченных Тевтонским орденом в XIII веке, и было зависимо до 1657 года от польских королей. В Тридцатилетней войне (1618-1648) относительно слабое владение Бранденбург-Пруссия увеличило свою территорию, в основном благодаря позиции Франции, видевшей в усилении Пруссии противовес влиянию Габсбургов. Курфюрст Фридрих-Вильгельм Великий (правил 1640—88 гг.) сумел превратить своё государство в сильную военную монархию с постоянной наёмной армией и сословным офицерским корпусом из низшего дворянства.
Нахождение герцогства Пруссии за пределами Священной империи позволило в 1701 преобразовать Бранденбург-Пруссию в королевство Пруссия.[1] В войнах XVIII века Пруссия значительно расширилась в результате завоевания Силезии у Габсбургов, захвата прибалтийского побережья у шведов, нескольких разделов Польши. К эпохе наполеоновских войн Пруссия вошла в число великих европейских держав, территориально единой и соперничающей с Австрией за влияние на германские дела.
Эпоха наполеоновских войн
Великая Французская революция вознесла к власти Наполеона, которому принадлежит заслуга в изменении политической географии Европы.
В войне 1799—1801 гг. Австрия потерпела поражение и вынужденно признала аннексию Францией германских земель на левом берегу Рейна. Чтобы возместить потери немецких князей, было решено кардинальным образом изменить структуру Священной Римской империи: обширные церковные владения, вольные города и мелкие государственные образования вошли в состав более крупных светских государств, число которых сократилось до 130 (число независимых уделов тем не менее составляло около 200). Священная Римская империя окончательно превратилась в конгломерат фактически независимых государств.
Формально Священная Римская империя прекратила существование после разгрома Австрии (называвшейся с 1804 года Австрийской империей) в войне 1805 года. 6 августа 1806 года император Франц II сложил с себя титул императора Священной Римской империи, оставшись императором Австрии. За месяц до того германские княжества объединились в Рейнский союз, где полновластным фактическим правителем стал Наполеон. Число германских государств в результате поглощения мелких владений сократилось до 40.
После разгрома в 1814 году Наполеона Рейнский союз был распущен, а вместо него образовалась конфедерация Германский союз из 38 немецких государств, включая Пруссию и немецкую часть Австрии. Территория Пруссии почти удвоилась за счёт анклава на Рейне, северной части королевства Саксония и польских земель, округливших её границы.
Многонациональная Австрийская империя с 27 млн подданных преобладала в союзе, однако преимущество Пруссии заключалось в том, что её 11-млн. население состояло в основном из немцев, а вновь присоединённые земли на Рейне обладали развитым промышленным потенциалом. Таким образом, ядром интеграционных процессов в Германии неизбежно становилась Пруссия.
Предпосылки объединения
Распространение германских языков (в том числе голландского и фламандского) на основе языкового картирования XIX века с наложенными современными границами государств
Из программного выступления в прусском парламенте премьер-министра Отто фон Бисмарка от 30 сентября 1862 года :
«Границы Пруссии в соответствии с Венскими соглашениями не благоприятствуют нормальной жизни государства; не речами и высочайшими постановлениями решаются важные вопросы современности — это была крупная ошибка 1848 и 1849 годов, — а железом и кровью»[2]
Общественно-политическая ситуация в Европе
После падения Наполеона в Европе возобладал принцип легитимизма, то есть признавалась нерушимость границ под властью традиционно правящих династий. Однако быстрое развитие капиталистического производства, парламентаризма и общественной мысли привели к пониманию приоритета интересов нации над монархо-династическими порядками. Буржуазия нуждалась в единых рынках сбыта, ей мешали феодальные границы и сословная структура общества. К середине XIX века в европейских народах возникло сильное стремление к созданию национальных государств, чему активно оказывали сопротивление уже сложившиеся империи.
В 1830 году Бельгия революционным путём отделилась от голландского королевства. В том же году и повторно в 1863 году поляки при моральной поддержке Англии и Франции поднимали восстания, с целью отделиться от Российской империи. В 1848 году Венгрия революционным путём вышла из Австрийской империи, однако интервенция российских войск разгромила революцию. В 1859 году началось объединение Италии вокруг североитальянского Пьемонта (Сардинского королевства). В том же году полузависимые от Турции княжества Молдавия и Валахия сблизились под единым правителем, а в 1862 году объединились в королевство Румыния. Национальное движение захватило Германию в 1848 году, но попытка начать объединение парламентским путём натолкнулась на отпор правящих классов, отвергающих революционные инициативы общества.
Стремление немцев к объединению. Революция 1848 года.
На берлинских баррикадах в марте 1848 года
В 1830-е годы в Германии началась индустриализация, породившая бурный экономический рост и обострившая конфликт интересов буржуазии с феодальным устройством общества. В 1834 году образовался Германский таможенный союз, куда вошли 12 германских государств и к 1860 году присоединились ещё 5.[3] Союз экономически объединял практически все крупные германские государства за исключением Австрии, устраняя таможенные барьеры между членами союза и накладывая повышенный единый тариф на товары из других стран.
В марте 1848 года по Германии, как и во Франции и Австрии, прокатилась волна выступлений, в том числе с уличными боями в Берлине, с требованием политических свобод и единой Германии. 18 мая 1848 года во Франкфурте-на-Майне по инициативе либеральной интеллигенции собралось Национальное всегерманское собрание, вошедшее в историю как Франкфуртский парламент. 28 марта 1849 года Франкфуртский парламент принял имперскую конституцию, по которой прусский король Фридрих Вильгельм IV должен был стать конституционным монархом Германской империи. Конституцию признали 29 германских государств, но не крупнейшие члены Германского союза (Пруссия, Австрия, Бавария, Ганновер, Саксония).
Фридрих Вильгельм IV отказался принять императорскую корону из рук революционного Франкфуртского парламента, Австрия и Пруссия отозвали оттуда делегатов. Лишившись политической поддержки верхов на фоне угасания революции, парламент распался. Часть делегатов добровольно покинула его, другая крайне левая часть была разогнана вюртембергскими войсками в Штутгарте в июне 1849 года. Волнения, вспыхнувшие в некоторых государствах, были подавлены прусскими войсками.
Прусский союз. Попытка объединения в 1849 году
Прусский король Фридрих Вильгельм IV отказался возглавить объединение Германии революционным путём «снизу», но желал совершить это «сверху», используя влияние, приобретённое при подавлении революции. В мае 1849 года он созвал конференцию, на которой Саксония и Ганновер вступили в федерацию Прусский союз (нем.)русск., где Пруссии отдавались внешняя политика и военные дела. Под влиянием настроений в обществе к Прусскому союзу примкнули 29 германских государств, кроме Австрии, Баварии, Вюртемберга и ещё нескольких княжеств (Эрфуртский союз (нем.)русск.).
Австрия противилась Прусскому союзу, но после революции 1848—1849 гг. не имела сил для военного противодействия. Поэтому в сентябре 1849 года она заключила с Пруссией соглашение о совместном управлении германскими делами. 10 мая 1850 года по инициативе Австрии был созван сейм Германского союза (Франкфуртский сейм), ознаменовавший восстановление прежних порядков в управлении Германией. Пруссия не признала сейм. Таким образом, два крупнейших германских государства шли к вооружённому конфликту при том, что остальные члены Германского союза разделились в своих симпатиях.
Противостояние осложнялось вялотекущей прусско-датской войной за независимость Гольштейна и внутренним конфликтом в Гессенском курфюршестве. Австро-баварский корпус по решению союзного сейма должен был подавить волнения в Гессене, но пруссаки не пропускали эти войска через свою территорию. 8 ноября 1850 г. произошло столкновение прусских и баварских войск у городка Бронцель под Фульдой (нем.)русск., в котором несколько человек были ранены. В конфликт вмешался царь Николай I, заставив Пруссию не препятствовать решениям общегерманского сейма. В итоге Пруссия под военным давлением Австрии и России подчинилась, отказавшись от идеи объединения Германии в рамках Прусского союза. Председатель прусского кабинета Мантейфель заявил об этом германским государям, сохранивших верность идее союза. По австро-прусскому соглашению (нем.)русск.[4] от 29 ноября 1850 года Пруссия устранилась от вмешательства в дела Гессена и Гольштейна, то есть фактически отказалась от независимой внутригерманской политики.
Австрии также не удалось воспользоваться дипломатической победой над Пруссией и усилить своё влияние на принятии решений по общегерманским делам.
Дрезденская конференция в декабре 1850 года восстановила прежние нормы отношений внутри Германского союза.
Попытка объединения Германии 1849 года закончилась неудачей из-за соперничества Пруссии с Австрией, сепаратистского настроя удельных германских правителей и вмешательства России.
Внешнеполитическая обстановка для Пруссии в 1860-х
Ни одна из великих держав стратегически не была заинтересована в возникновении в центре Европы нового мощного государства, хотя никто не предвидел тогда в полной мере угрозы германского милитаризма. В то же время к середине 1860-х годов благодаря последовательной дипломатии Бисмарка и политической разобщённости великих держав (самоустранение России от международных дел после Крымской войны; экспансия Франции при Наполеоне III, повлёкшая разногласия с Англией и Австрией; борьба Австрии с объединённой Италией) создалась благоприятная внешняя обстановка для объединения Германии вокруг Пруссии.
- Среди событий в России, предшествующих началу объединения, следует отметить Крымскую войну 1853—56 гг. и Польское восстание 1863 года. В результате поражения в Крымской войне влияние России в Европе ослабло, отношение России к её противникам Англии, Франции и особенно Австрии оказалось надолго испорченным.[5] Пруссия была единственной великой державой, которая не выступила против России, что вместе с прусской помощью в подавлении Польского восстания 1863 года[6] обеспечило благожелательный нейтралитет Российской империи в войнах Пруссии против соседей. Также прусский король Вильгельм I приходился дядей царю Александру II, что также склоняло позицию России в пользу Пруссии.
- Ведущая держава Европы на то время Франция завязла в 1862—65 гг. в оказавшейся провальной мексиканской войне. Её силы были отвлечены на захват и укрепление колоний, где французские интересы постоянно сталкивались с английскими. На это наложились личные антипатии императора Наполеона III к Англии в силу подозрений, что итальянские заговорщики используют английскую территорию для подготовки покушений на его жизнь. Сближение Франции с Австрией и тем более союз были невозможны из-за объединения Италии, в ходе которого французская армия в 1859 году сражалась с австрийской. Наполеон III недооценивал военную силу модернизированного прусского государства и надеялся только выиграть в качестве арбитра от внутригерманского конфликта.
- Англия, владевшая огромной колониальной империей, не была расположена вмешиваться без крайней необходимости в дела Европы. Тем более, что морской державе было затруднительно воевать без союзников на континенте, а именно в сильной Пруссии правящая элита видела поначалу противовес Французской империи. Англичан сильно беспокоил как французский проект Суэцкого канала (опасения за Индию), так и стремление Наполеона III присоединить Бельгию. К тому же объединённая Германия не рассматривалась в качестве соперника Англии в колониальных делах, но могла быть выгодным торговым партнером для сбыта английской продукции и колониальных товаров.
- Австрия не могла стать лидером в деле объединения Германии из-за внутренних и внешних конфликтов, хотя идея великогерманского объединения (то есть включая Австрию) имела немало сторонников. Внутренние субъекты Австрийской империи, особенно венгры, вовсе не желали дальнейшего усиления немецкого доминирования, опасаясь потерять свою автономию. Да и сами немцы из северной Германии не стремились к единению с многонациональным государством. Объединение Италии шло в том числе за счёт австрийских владений с италоязычным населением, что отвлекало силы империи на юг.
Внутриполитическая обстановка в Пруссии в 1860-х
Прусский триумвират 1860-х годов, превративший Германию во второй половине XIX века сначала в региональную, а затем и в мировую великую державу. Слева направо: «железный канцлер» Отто фон Бисмарк; военный министр Пруссии, реформатор армии и его ближайший соратник Альбрехт фон Роон; видный деятель военной науки, бессменный начальник Генерального штаба Хельмут фон Мольтке
7 октября 1858 года к власти в Пруссии пришёл в качестве регента 60-летний принц Вильгельм, брат впавшего в слабоумие короля Фридриха Вильгельма IV. После его смерти 2 января 1861 года Вильгельм стал прусским королём.
Под его руководством началась военная реформа, которая восстанавливала всеобщую воинскую повинность на 3 года[7], что увеличило численность постоянной армии до 400 тыс. человек. При этом отпадала необходимость рассчитывать на ополчение-ландвер с его низкой боеспособностью. Содержание большой профессиональной армии обходилось дорого, ландтаг (нижняя палата прусского парламента) отказался утвердить расходы на это.
Вильгельм I распустил ландтаг, но повторные выборы 1862 года собрали ещё более радикальных депутатов. Назрел конституционный кризис, для разрешения которого король утвердил 8 октября 1862 года главой исполнительной власти прусского посла в Париже Отто фон Бисмарка. Новый канцлер решился управлять Пруссией без одобренного бюджета, что являлось прямым нарушением конституции. Ландтаг, выражавший интересы прежде всего национальной буржуазии, в очередной раз был распущен в 1863 году, в стране началось волнение.
Бисмарк сохранял спокойствие, он был уверен, что победоносная внешняя политика погасит внутриполитический конфликт. Удобный случай представился со смертью датского короля Фредерика VII в 1863 году, после чего Пруссия победила в Датско-прусской войне 1864 года. В начале июля 1866 года в разгар победоносной войны с Австрией прошли очередные выборы в прусский ландтаг. Большинство в ландтаге завоевали представители национал-либеральных течений, которые утвердили все расходы, сделанные прусским правительством и не одобренные ранее ландтагом. Таким образом Бисмарку удалось погасить конфликт и сохранить конституционную форму прусской монархии.
Датско-прусская война 1864 года
Бисмарк не имел определённого чёткого плана объединения Германии. Он видел главную цель и шёл к ней последовательно, используя любую возможность. При этом Бисмарк предпочитал действовать политическими методами, но не избегал военных решений, если это приближало его к главной цели. Исторически сложилось так, что датско-прусская война 1864 года стала первым шагом на пути объединения Германии.
Хотя Австрия и Пруссия действовали как союзники против Дании, на деле конфликт превратился в пробу сил между ними за право возглавить интеграционный процесс в Германии. Успех Пруссии в таком рискованном деле, как изменение баланса сил в Европе в пользу Германского союза, укрепил позиции Бисмарка (бывшего всего лишь государственным прусским чиновником высшего ранга) и обеспечил поддержку германским обществом его начинаний.
Причины датско-германского конфликта
Прусско-датский конфликт из-за независимости герцогств Шлезвига и Гольштейна,[8] находившихся под властью датского короля, начался в революционном 1848 году. Вмешательство великих держав заставило Пруссию и Австрию признать по Лондонскому протоколу (от 8 мая 1852 года) наследственные права датской короны на эти княжества.
Кроме чувства национального единства, требующего присоединения к Германскому союзу земель с немецким населением, у Пруссии был стратегический интерес к территории Гольштейна. Там располагались удобные гавани на Балтике, a через его земли в основании Ютландского полуострова можно было прорыть канал, значительно сокращавший морской путь из Северного моря в Балтийское.
Датский король Фредерик VII умер 15 ноября 1863 года, не оставив сына, что дало Германскому союзу формальный повод оспорить наследственные права Дании на территорию герцогств. Новый король Дании Кристиан IX подписал 18 ноября 1863 года конституцию, по которой полиэтничный Шлезвиг, бывший веками фактически частью Дании, присоединялся к Дании. Гольштейн, входящий в Германский союз, сохранял свой государственный статус под властью датской короны. Пруссия и Германский союз немедленно усмотрели в присоединении одного только Шлезвига нарушение средневековой нормы и Лондонского протокола, по которым закреплялось обязательство Дании сохранять политическое единство Шлезвиг-Гольштейна. Повод для второй войны за Шлезвиг-Гольштейн был найден.
Начало датско-германской войны
Фридрих Августенбургский из побочной ветви датской королевской династии заявил права на престол герцогств, Германский сейм поддержал его как человека, близкого по духу к германской нации. 24 декабря 1863 года войска Саксонии и Ганновера, выполняя решение Германского союза, заняли территорию Гольштейна.
Бисмарку удалось представить свой тайный план расширения Пруссии как внутригерманское дело, как борьбу за независимость герцогств в рамках сохранения их прежнего государственного статуса. Он публично не поддержал резолюцию сейма и не признал прав Фридриха, за что подвергся резкой критике в Пруссии. Усыпив бдительность великих держав, Бисмарк втянул Австрию в антидатскую коалицию. 16 января 1864 года Пруссия и Австрия предъявили Дании ультиматум: в 48 часов отменить конституцию. Датское правительство отклонило ультиматум, надеясь на вмешательство Англии и Франции. 1 февраля 1864 года в Шлезвиге начались боевые действия.
Победа австро-прусской коалиции
Австро-прусская коалиция с участием других германских государств была слишком сильной, чтобы Англия могла решиться воевать за Данию в одиночку. Английский премьер Пальмерстон обратился к Франции с предложением вмешаться в шлезвиг-гольштейновский вопрос, однако Франция ответила отказом. После провала в Мексике Франция не желала нового конфликта, причем в союзе с Англией, которая ничем не рисковала. Французский император Наполеон III помнил о неудачном дипломатическом выступлении совместно с Англией против России по поводу польского восстания 1863 года, когда Англия решительно толкала союзника на войну с Россией, но сама внезапно дала задний ход. Раздражение Наполеона вызвал также визит в апреле 1864 года в Англию известного итальянского революционера Гарибальди.
1 августа 1864 года Дания, убедившись, что реальной помощи ждать не приходится, подписала предварительные условия мира. Датский король уступил все права на спорные герцогства Гольштейн, Шлезвиг и Лауэнбург в пользу короля Пруссии и императора Австрии.
Венский договор от 30 октября 1864 года формально закрепил уменьшение датских владений в Европе на 40 %. Бисмарку удалось отстранить от власти Фридриха Августенбургского, в пользу которого Германия выступала вначале единым фронтом и под прикрытием которого Бисмарк спланировал аннексию завоёванных земель. 14 августа 1865 года по Гаштейнской конвенции Австрия и Пруссия, сохраняя право общей собственности над герцогствами, разделили управление над ними: Шлезвиг поступил в управление Пруссии, Гольштейн достался Австрии. Самый маленький Лауэнбург был предоставлен в собственность Пруссии за 2,5 млн талеров, уплаченных Австрии.
Гаштейнская конвенция не столько разрешала проблему раздела добычи между Австрией и Пруссией, сколько создала новый повод для войны между ними.
Австро-прусская война 1866 года
Подготовка австро-прусской войны
Объединение Германии неизбежно должно было привести к войне Пруссии с Австрией, Бисмарк предвидел это ещё в 1856 году:
«Германия слишком тесна для Австрии и Пруссии. Поэтому в близком будущем нам придется отстаивать против Австрии наше право на существование, и не от нас зависит избежать конфликта; течение событий в Германии не допускает другого исхода.»[9]
Делёж Шлезвига и Гольштейна был сознательно выбран Бисмарком как удачный повод к войне с Австрией. Во-первых, конфликт из-за герцогств снижал вероятность вмешательства других держав на стороне Австрии; во-вторых, в случае победы оба герцогства отходили к Пруссии как дополнительный трофей помимо главного выигрыша — гегемонии в германских делах.
Обладание Гольштейном при неясных условиях совместной собственности по Гаштейнской конвенции скорее создавало проблемы Австрии, чем давало ей выгоды, так как это герцогство было отделено от империи прусской территорией. Попытка Австрии урегулировать вопрос путём обмена Гольштейна на скромную территорию в районе прусско-австрийской границы натолкнулась на категорический отказ Бисмарка. К февралю 1866 года он решился на войну, крайне непопулярную как в Германии, так и среди прусского общества. Впоследствии начальник прусского генерального штаба Гельмут фон Мольтке писал:
«Война 1866 года не была вызвана необходимостью отразить угрозу нашему национальному существованию; это был конфликт, признанный необходимым в кабинете, заранее обдуманный и постепенно подготовлявшийся.»[10]
Ставка и риск были настолько высоки, что в случае поражения Бисмарк был готов расстаться с жизнью. Летом 1866 года он заявил английскому посланнику:
«Может статься, Пруссия проиграет, но в любом случае, она будет сражаться отважно и с честью… Если нас разобьют, я не вернусь сюда. Я погибну в последней атаке. Умереть можно лишь однажды, и побежденному лучше всего умереть.»[2]
Дипломатическая активность Бисмарка
Свои усилия Бисмарк направил сразу по нескольким направлениям.
- Нейтралитет России. Царь Александр II благожелательно относился к Пруссии, единственной из великих держав не выступивших против России в Крымской войне. Бисмарк ещё более завоевал доверие царя обещанием в 1866 года поддержать требование России об отмене статьи Парижского договора 1856 года, которая запрещала России иметь Черноморский военный флот.
- Нейтралитет Франции. Противоречия Франции с Австрией не перевешивали того обстоятельства, что политически объединённая Германия являлась серьёзной угрозой национальной безопасности Франции. Бисмарк осенью 1865 года встретился с Наполеоном III на морском курорте в Биаррице, где предложил Франции герцогство Люксембург в обмен за нейтралитет. Наполеон ясно дал понять, что желает большего, а именно Бельгийское королевство. Такое усиление Франции не входило в планы Бисмарка, он предпочёл взять паузу в государственном торге.
Франция продолжала оставаться самой серьёзной угрозой прусской экспансии. Наполеон III рассчитывал не мешать австро-прусской войне, дождаться ослабления обоих противников в их изнурительном противостоянии, а затем получить без особого риска Бельгию заодно с Люксембургом, просто придвинув французскую армию к Рейну. Бисмарк правильно оценил намерения французского императора и постарался использовать это в плане военной кампании против Австрии. Успех могла принести только быстрая кампания, чтобы успеть высвободить прусскую армию прежде, чем Наполеон III решится вступить в конфликт. Для этого необходимо было ослабить австрийскую армию войной на два фронта.
- Союз с Италией. Бисмарк использовал недовольство образованного в 1861 году Итальянского королевства тем, что Австрия продолжала удерживать область Венеции. Бисмарк дал обязательство королю Виктору-Эммануилу II отдать ему Венецию при любом исходе войны Италии с Австрией. Однако Наполеон III запретил зависимому от него итальянскому королю союз с Пруссией, и только после долгих уговоров Бисмарка снял возражение. 8 апреля 1866 года был подписан союзный договор, по которому Италия должна была напасть на Австрию, если Пруссия начнёт войну в 3-месячный срок.
Ход боевых действий
7 июня 1866 года прусские войска стали занимать Гольштейн под предлогом прекращения там антипрусской агитации. 14 июня Австрия при поддержке других крупных государств Германского союза провела решение на общегерманском сейме о мобилизации войск против Пруссии. Бисмарк обратился к немецкому народу с речью, в которой представил Пруссию жертвой австрийской агрессии, вызванной прусским предложением о реформировании Германского союза в сторону более тесного единства. 16 июня прусские дивизии пересекли границы австрийской Богемии и других германских государств, союзных Австрии. 20 июня в войну против Австрии вступила Италия.
Фактически расстановка сил выглядела следующим образом: Пруссия в союзе с Италией против Австрии с Саксонией. Союзниками Пруссии были мелкие северо-германские государства (Мекленбург, Гамбург, Ольденбург, Бремен и др.). Союзниками Австрии выступили крупные государства Германского союза Бавария, Ганновер, Саксония, Вюртемберг, Баден, Гессен, Франкфурт и др., но сколько-нибудь значимые вооружённые силы (более 20 тыс.) выставила только Саксония.
Уже 24 июня 1866 года относительно большая итальянская армия побежала после битвы при Кустоце, но свою роль она выполнила, оттянув на юг 78-тыс. австрийскую армию.
Пруссии пришлось иметь дело с 3 группировками противника. Австрия и Саксония на юге; Бавария и Вюртемберг на юго-западе; Ганновер, Гессен и Кассель на западе. Германские войска не доставили особых хлопот пруссакам. 29 июня капитулировала ганноверская армия, после чего 3 прусские дивизии (48 тыс.) повернули на южногерманские государства, которые не успели отмобилизовать силы. Успешное продвижение пруссаков в Баварии было остановлено лишь наступившим перемирием.
Основные события разворачивались в Богемии (Чехии), где 280-тыс. прусской армии противостояла немногим более слабая австрийская группировка. В ряде сражений австрийцы потерпели поражение, их деморализованные войска откатились от границы. Уже 1 июля австрийский командующий Бенедек попросил императора Франца-Иосифа скорее заключить мир. 3 июля в битве при Садовой (при Кёниггреце) в верховьях Эльбы пруссаки разгромили главную австрийскую армию и к середине июля вышли на подступы к Вене. Очень неспокойно было в Венгрии, жители которой готовились к отделению от Австрийской империи. Хотя австрийцы имели ещё достаточно войск для продолжения войны, дальнейшее сопротивление могло привести империю к развалу.
Бисмарк, преодолевая недовольство своего короля и прусского генералитета, спешил с необременительным для Австрии миром по другим соображениям: Россия и Франция могли увеличить цену за свой нейтралитет. Министр иностранных дел Франции выступал за немедленное нападение на Пруссию. Наполеон III, смущённый быстрым разгромом австрийцев, колебался, тем не менее за несколько дней до перемирия французский посол в Берлине предложил Пруссии согласиться на аннексию Люксембурга. Война окончилась быстрее, чем великие державы успели опомниться. 26 июля 1866 года в Никольсбурге при посредничестве Франции был подписан предварительный мир.
Во время мирных переговоров 16 августа Наполеон III через посла в Берлине предложил Бисмарку заключить секретный наступательный и оборонительный союз, условием которого было присоединение Бельгии и Люксембурга к Франции. Бисмарк сделал вид, что готов примириться с будущим усилением Франции, но фактически затянул рассмотрение вопроса. Тем временем 23 августа 1866 года в Праге был заключён окончательный мирный договор с Австрией.
Результат австро-прусской войны
- Главным результатом победы Пруссии стал выход Австрии из Германского союза. Последующее создание Северогерманского союза и присоединение 12 января 1867 года Шлезвига-Гольштейна к Пруссии явились логичным завершением устранения Австрии от германских дел.
- Венеция была присоединена к Итальянскому королевству, хотя нельзя считать это непосредственным результатом боевых действий. Ещё до начала войны 12 июня 1866 Австрия согласилась уступить Венецию французскому императору с тем, чтобы он передал её своему союзнику королю Виктору Эммануилу II. Однако итальянцы все равно решились воевать, формально соблюдая условия прусско-итальянского договора, но фактически надеясь на более значительные территориальные приобретения.
- Бисмарк сознательно отказался от территориальных приобретений за счёт Австрии, не желая возбуждать в ней жажды реванша. На Австрию была наложена необременительная контрибуция.
- Сильнее пострадали германские союзники Австрии. Бавария и Гессен-Дармштадт уступили Пруссии часть своих земель к северу от реки Майн.[11] Пруссия присоединила в сентябре 1866 года королевство Ганновер, курфюршество Гессен-Кассель, герцогство Нассау и город Франкфурт. Саксония избежала поглощения только благодаря требованию Австрии. Прусское королевство в 1867 года стало насчитывать 24 млн жителей.
Северогерманский союз. 1867—1870 годы
Образование Северогерманского союза
Население присоединённых земель, за исключением датскоговорящих жителей северного Шлезвига, лояльно восприняли аннексию Пруссией своих государств. Лишённые владений удельные монархи получили богатые доходы в качестве компенсации, если только не пытались бороться за реставрацию. На сохранивших независимость мелких монархов северной Германии Пруссия надавила, чтобы создать военно-политический Северогерманский союз.
4 августа 1866 года Бисмарк предложил государствам Северной Германии (21 государство с 6 млн жителей, самое крупное — королевство Саксония) заключить союз с Пруссией на год, в течение которого должны быть выработаны принципы объединения. Берлинская конференция (13 декабря 1866 — 9 января 1867) утвердила гегемонию Пруссии в Северогерманском союзе, построенном по федеративному принципу.
Главой союза стал прусский король, он же верховный главнокомандующий вооружёнными силами всех государств, входящих в союз. Прусский король получил право от имени союза объявлять войну, вести переговоры и заключать мир. В ведение союзных органов перешли транспортные коммуникации, монетное дело, уголовные дела, часть налогов. Все войска перестраивались под прусский образец. Союзный парламент (рейхстаг) избирался прямым голосованием, но получил ограниченные полномочия. Большим влиянием на государственные дела пользовался союзный совет (бундесрат), состоявший из представителей государей. Пруссия, несмотря на преобладающую численность своих подданных в союзе, имела в совете лишь 17 голосов из 43.
1 июля 1867 года союзная конституция была опубликована, а осенью начал действовать избранный рейхстаг. За время своего недолгого существования (1867—1871 гг.) он провёл существенную работу по укреплению политического единства Северогерманского союза. В экономическом плане принятые законы окончательно порушили старые феодальные порядки с ограничениями (отмена монополий, снятие всевозможных запретов и средневековых регламентов, свобода переселения внутри союза, право на забастовки).
Южногерманские государства
В дела германских государств к югу от Майна Пруссия не вмешивалась, чтобы не возбуждать опасений Франции. По Пражскому договору 1866 года эти государства (Бавария, Вюртемберг, Гессен-Дармштадт, Баден, всего около 6 млн жителей) должны регулировать отношения с Северогерманским союзом специальными соглашениями.
Осознав угрозу существования в политической изоляции, эти государства заключили с Северогерманским союзом тайные договоры оборонительного характера. Стороны гарантировали неприкосновенность своих владений и в случае войны должны были объединить армии. Депутаты южногерманских государств допускались в союзный рейхстаг для обсуждения торговых и экономических вопросов в рамках общегерманского таможенного союза.
Политическая ситуация в Германии в 1870 году
Настроения жителей южногерманских государств (за исключением Бадена) не способствовали объединению с Северогерманским союзом. Католики юга Германии с подозрением относились к протестантам севера, а правящие элиты не желали жертвовать властью в пользу идеи германского единства. Промышленно менее развитый регион по сравнению с северной Германией не имел сильной мотивации к созданию единого рынка или сильной империи для захвата колоний.
В мае 1868 года Бисмарк заявил:
«Все мы носим в сердце идею национального единения, однако для расчётливого политика на первом месте всегда необходимое, а уже потом желательное, то есть вначале оборудование дома, а только потом его расширение. Если Германия реализует свои национальные устремления до окончания девятнадцатого века, я сочту это величайшим событием, а случись то же самое через десять или даже пять лет — это было бы нечто из ряда вон выходящее, неожиданная милость божья.»[2]
Однако с началом Франко-прусской войны все политические преграды в июле 1870 года были сметены взрывом патриотического энтузиазма среди немцев.
Франко-прусская война 1870—71 годов
В 1867 году на границах Франции возникло сильное федеративное государство Северогерманский союз с 24 млн пруссаков и 6 млн других немцев. Ещё 6 млн немцев из южногерманских государств были связаны с союзом договорными обязательствами. Франция ничего не получила в качестве компенсации от создания мощного германского государства, по количеству жителей сравнимого с населением Франции (36 млн французов). На это наложились внутриполитические проблемы в империи Наполеона III и заинтересованность Пруссии в присоединении южногерманских королевств. Обе державы стремились решить свои внутренние проблемы победоносной войной друг с другом.
Причины, подготовка и ход войны с приведёнными цитатами изложены в целом по сборнику «История дипломатии» под ред. В. П. Потемкина и статье в ЭСБЭ[12].
Франко-прусская война
К лету 1870 года Наполеон III почувствовал неустойчивость своего положения внутри Франции.[13] Его влиятельная жена императрица Евгения говорила, указывая на сына: «Война необходима, чтобы это дитя царствовало.» Попытки договориться с Бисмарком об аннексии Люксембурга и тем более ельгии закончились ничем, экспансия Французской империи в Европе могла произойти только военным путём.
Повод к конфликту возник 1 июля 1870 года, когда испанцы пригласили на королевский престол принца Леопольда из боковой ветви правящей прусской династии Гогенцоллерн-Зигмаринген. Французы не без оснований усмотрели угрозу в правлении династии Гогенцоллернов одновременно в Германии и Испании. 6 июля министр иностранных дел Франции герцог Грамон заявил в парламенте, что Французская империя без колебаний начнёт войну против Пруссии, если та «посмеет воскресить империю Карла V»[14].
Бисмарк рассматривал давление Франции как удобный повод для войны, в которой Пруссия оказалась бы в роли жертвы агрессивного соседа, но прусский король Вильгельм I заставил своего родственника Леопольда официально отказаться от испанского престола. Тем не менее, Наполеон III под влиянием ближайшего окружения и ложного представления о состоянии французской армии решил ускорить события. 13 июля Париж потребовал от Вильгельма письменного заявления с обязательством не вредить в будущем интересам Франции. Требование содержало преднамеренную дерзость, и прусский король отказался дать подобные гарантии, пообещав продолжить переговоры.
Бисмарк после консультации с начальником генштаба и военным министром самовольно изменил текст о ходе переговоров для сообщения в прессе таким образом, что будто Вильгельм отказался вообще обсуждать вопрос с французским послом. Французы восприняли это именно так, как рассчитывал Бисмарк, и к чему стремился Наполеон III.
Династический спор заинтересованные стороны превратили в повод к войне, причина которой состояла в борьбе за политическое господство в западной Европе. 15 июля депутаты французского парламента 245 голосами против 10 одобрили объявление войны. 19 июля 1870 года на заседании северогерманского рейхстага Бисмарк объявил о начале войны Франции против Пруссии.
Внешнеполитическая ситуация для Франции и Пруссии
- Позиция России. Хотя Александр II с неудовольствием следил за поглощением мелких германских государств Пруссией, вызывающие требования Наполеона III к Вильгельму I рассердили царя. Более существенным являлось обещание Бисмарка поддержать Россию в пересмотре Парижского договора 1856 года, запрещавшего России иметь Черноморский военный флот. 23 июля была опубликована декларация России о нейтралитете с призывом к другим государствам о невмешательстве во франко-прусскую войну.
- Внутри Австро-Венгрии боролись два течения: военно-аристократические круги желали реванша над Пруссией, в то время как буржуазия и венгерские националисты выступали против. Исход противостояния в правящих кругах был решён позицией Александра II. Австрийцам дали понять, что на их вмешательство Россия ответит открытием военных действий против Австро-Венгрии.
- Англия заявила о своём нейтралитете ещё 18 июля. Бисмарк постарался закрепить эту позицию, обнародовав 24 июля конфиденциальную записку французского посла в Пруссии от 1867 года, в которой посол развивал проект захвата Бельгии Францией. Общественное мнение англичан было настроено резко против личности Наполеона III, хотя правительство и видело опасность в чрезмерном усилении Пруссии.
- Итальянский король Виктор-Эммануил склонялся к союзу с Францией, однако этому препятствовало нахождение французского гарнизона в Риме. Франция поддерживала папское государство, из-за чего объединение Италии не могло быть завершено. Бисмарк шантажировал Виктор-Эммануила, угрожая поддержать деньгами и оружием республиканское восстание в случае выступления Италии на стороне Франции. После поражения Франции итальянцы предпочли извлечь из этого выгоду и заняли 20 сентября 1870 года Рим, покинутый французскими войсками.
Ход боевых и дипломатических действий
Одно из сражений (при Марс-ла-Тур) франко-прусской войны в августе 1870 года
28 июля 1870 года Наполеон III прибыл в Мец, чтобы повести французскую армию в Пруссию. Однако он обнаружил полную неготовность войск к ведению войны и был вынужден остаться на границе, дожидаясь окончания мобилизации. Инициатива перешла к пруссакам, которые быстро сосредоточили 3 армии (330 тыс. солдат) и двинули их 4 августа во Францию. Французские войска в приграничных районах значительно уступали противнику в численности (200 тыс. солдат), тактической подготовке и артиллерии.
Основная французская группировка (180 тыс.) под командованием маршала Базена была блокирована под Мецем, на её выручку двинулась другая армия (140 тыс.) под командованием маршала Мак-Магона и при которой находился Наполеон III. Эта армия была окружена под Седаном. 1 сентября произошло сражение, а на следующий день после неудачных попыток прорыва император Наполеон III сдался вместе с более чем 100 тыс. своих солдат. Армия Базена капитулировала позднее, 27 октября 1870 года.
После получения известия о пленении Наполеона 4 сентября в Париже была объявлена республика и организовано правительство национальной обороны. Пруссия нарастила численность войск во Франции до 700 тыс. солдат, в октябре был блокирован Париж. 28 января 1871 года Париж капитулировал, затем во Франции были проведены выборы в Национальное собрание, которое утвердило 10 мая 1871 года окончательный мир (Франкфуртский мир) с Пруссией, фактически с провозглашённой Германской империей.
Объединённая Германия
Объединение германских государств
С началом войны немцы из южногерманских государств сразу встали на сторону Пруссии. Студенты записывались волонтёрами в армию, попытки сохранить нейтралитет пресекались общественным мнением. Победы прусской армии во Франции вызвали небывалый подъём национального самосознания, на волне которого идея германского единства претворилась в жизнь.
После победы под Седаном южногерманские государства начали с Пруссией переговоры о вступлении в Северогерманский союз. Герцогство Баден ещё до войны собиралось присоединиться к союзу, переговоры с королевствами Баварией и Вюртембергом осложнялись тем, что эти государства претендовали на особые привилегии внутри союза. Король Баварии Людвиг II согласился признать прусского короля своим сюзереном за солидное пенсионное обеспечение в виде ежегодных выплат в размере 300 тыс. марок золотом.[2] 23 ноября 1870 года подписан договор между Северогерманским союзом и Баварией, оговорившей её военную автономию в мирное время. 25 ноября в союз вступил Вюртемберг, армия которого составила отдельный корпус в вооружённых силах Германии.
10 декабря 1870 года рейхстаг Северогерманского союза по предложению канцлера Северогерманского союза Бисмарка от 9 декабря 1870 года переименовал Северогерманский союз в Германскую империю, конституцию Северогерманского союза — в конституцию Германской империи, а пост президента Северогерманского союза — в пост германского императора[15]
Бисмарк организовал письмо от германских государей с просьбой Вильгельму I принять из их рук императорскую корону. 18 января 1871 года в Версальском дворце под Парижем Бисмарк в присутствии немецких князей зачитал текст провозглашения прусского короля германским императором. Депутаты представительного органа немецкого народа, рейхстага, участия в церемонии не принимали.
21 марта 1871 года собралось первое заседание Германского рейхстага, а 16 апреля была принята конституция Германской империи, по сути, модифицированная версия конституции упразднённого Северогерманского союза.
Германская империя
Германская империя (Deutsches Reich) объединила политически все государства с немецким населением за исключением Австрии, Люксембурга и Лихтенштейна. Эти 25 государств с 36 млн немцев обладали различными правами и неодинаковым влиянием внутри империи. Отдельные удельные монархи сохранили свою самостоятельность на местном уровне, они также имели влияние через назначение представителей с правом вето в верхнюю палату германского парламента.
Выборы в нижнюю палату, рейхстаг, проводились по принципу всеобщего равного избирательного права для мужчин, однако демократический характер процедуры не соответствовал возможностям низших классов влиять на управление государством, так как реальная власть сосредоточилась в руках императора.
Франкфуртский мир с Францией (10 мая 1871 года) прибавил 26-й субъект в империю: Эльзас-Лотарингию (1,5 млн жителей), непосредственно подчиненную имперскому правительству.
Примечания
- ↑ Внутри Священной империи никто из её субъектов не мог носить титул короля, который подразумевал независимость от императора.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Хилльгрубер А. Выдающиеся политики: Отто фон Бисмарк, Меттерних. — Ростов-на-Дону: Феникс, 1998
- ↑ Единые таможенные правила были введены Пруссией в 1818 году, затем к ним постепенно присоединялись другие германские государства. Гамбург и Бремен присоединились последними в 1888 году уже после образования Германской империи.
- ↑ Соглашение, заключённое в Ольмюце 29 ноября 1850 года, известно в истории дипломатии как Ольмюцкое унижение Пруссии. Несмотря на то, что соглашение предотвратило австро-прусскую войну с Россией на стороне Австрии, в Пруссии восприняли его как капитуляцию, а прусские историки драматизировали соглашение как национальный позор.
- ↑ Хотя австрийские войска не участвовали в боевых действиях Крымской войны, Австрия выдвинула ультиматум России, что было расценено царём и русским обществом как предательство.
- ↑ Пруссия разрешила царским войскам преследовать польских повстанцев на своей территории.
- ↑ Всеобщая воинская повинность была введена в Пруссии в 1813 в период войны с Наполеоном. Позднее фактически не исполнялась.
- ↑ Гольштейн с полностью немецким населением входил в Германский союз. Шлезвиг примыкал к югу Дании и имел на севере преобладание датского населения. Оба герцогства считались наследственными владениями короля Дании, причем в 1460 году]] датский король Кристиан I взял обязательство политически не разъединять герцогства и не присоединять их к Дании.
- ↑ Докладная записка Бисмарка от 26 апреля 1856 года. Цитата из книги Э. Лависс, А. Рамбо, « История XIX века»
- ↑ Э. Лависс, А. Рамбо, « История XIX века», т. 5, ч. 1, гл. 8
- ↑ Река Майн была определена как граница, южнее которой прусская экспансия затрагивала бы интересы Франции.
- ↑ Франко-прусская или франко-германская война 1870—1871 гг. // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907.
- ↑ Во Франции набирали силу сторонники республики. Так в январе 1870 в Париже прошла 200-тыс. антиправительственная демонстрация в знак протеста против убийства журналиста-республиканца.
- ↑ Имеется в виду император Священной Римской империи Карл V, бывший в начале XVI века одновременно королём Испании.
- ↑ перевод с http://www.documentarchiv.de/ksr/dtrdtk.html
Ссылки и источники
- Чудовский В. Н. Война за Шлезвиг-Гольштейн 1864 года на сайте Руниверс
- Процесс объединения Германии (ход событий, ключевые даты, анализ политики) описан в общих чертах по следующим источникам:
- Эрнест Лависс, Альфред Рамбо, «История XIX века», т. 5, ч. 1, гл. 8 : Объединение Германии.
- История дипломатии, Том I, раздел 4, главы 12-14 / Под ред. Потемкина В.П. — М.: ОГИЗ, 1941. Архивировано 27 сентября 2007 года.